With the rapid adoption of multimodal large language models (MLMs) in autonomous agents, cross-platform task execution capabilities in educational settings have garnered significant attention. However, existing benchmark frameworks still exhibit notable deficiencies in supporting cross-platform tasks in educational contexts, especially when dealing with school-specific software (such as XiaoYa Intelligent Assistant, HuaShi XiaZi, etc.), where the efficiency of agents often significantly decreases due to a lack of understanding of the structural specifics of these private-domain software. Additionally, current evaluation methods heavily rely on coarsegrained metrics like goal orientation or trajectory matching, making it challenging to capture the detailed execution and efficiency of agents in complex tasks. To address these issues, we propose KGCE (Knowledge-Augmented Dual-Graph Evaluator for Cross-Platform Educational Agent Benchmarking with Multimodal Language Models), a novel benchmarking platform that integrates knowledge base enhancement and a dual-graph evaluation framework. We first constructed a dataset comprising 104 education-related tasks, covering Windows, Android, and cross-platform collaborative tasks. KGCE introduces a dual-graph evaluation framework that decomposes tasks into multiple sub-goals and verifies their completion status, providing fine-grained evaluation metrics. To overcome the execution bottlenecks of existing agents in private-domain tasks, we developed an enhanced agent system incorporating a knowledge base specific to school-specific software. The code can be found at https://github.com/Kinginlife/KGCE.
The rapid advancement of multimodal large language models (MLMs) is reshaping the capability boundaries of autonomous agents, driving them from single-environment task execution towards cross-platform collaboration [1]. Represented by models like GPT-4o, MLMs integrate visual, linguistic, and action-reasoning capabilities, demonstrating significant potential in general scenarios such as cross-device file transfer and multi-application collaborative operations.
Existing agents have predominantly focused on generic scenarios such as scientific research [2] and code generation [3]. However, their performance often declines sharply when transitioning to educational settings due to two major bottlenecks: lack of domain-specific knowledge and misalignment with assessment frameworks. Educational environments Fig. 1.
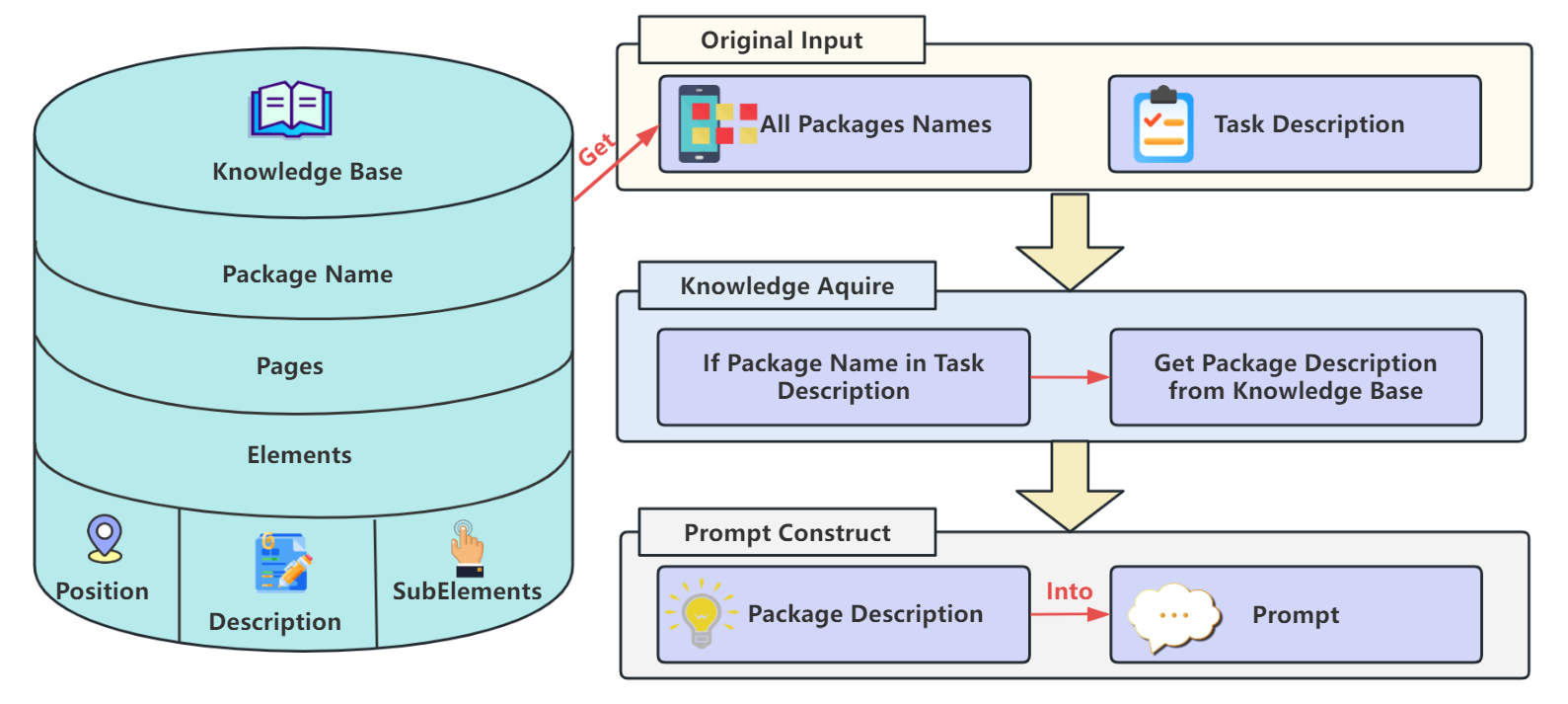
The overall framework of KGCE. The system first generates tasks from educational datasets, then executes them through a pipeline of action prediction, execution, and evaluation. A dual-graph evaluator assesses task completeness and execution efficiency. Based on screenshot and OCR feedback, the system may invoke external knowledge from LLMs (e.g., GPT-4o, Qwen-VL, Gemini) to support cross-environment agents (Windows and Android) in accomplishing complex tasks. pose unique challenges: (1) they heavily rely on schoolcustomized software, characterized by closed private-domain features that lack standardization in interface elements and operational logic; (2) cross-platform tasks require coordination across multiple devices like Windows and Android, involving complex process dependencies and state synchronization; (3) task objectives combine functional requirements with educational significance, demanding agents to exhibit both operational accuracy and cognitive understanding of educational contexts. Current research has yet to effectively address these challenges, thus limiting the practical deployment of educational agents.
Existing work exhibits significant limitations in three key areas. Currently, there is a lack of task datasets tailored for educational agents, which hampers research and development in educational scenarios. Existing knowledge graphs [13] and GUI operation libraries [6] are primarily designed for general-purpose software and cannot provide structured knowledge support for school-specific systems. Conventional metrics, such as task completion rate and trajectory similarity, focus solely on macroscopic outcomes. These metrics cannot quantify fine-grained issues like backtracking operations or omissions of critical steps.
To address the the above issues, we propose Knowledge-Augmented Dual-Graph Evaluator for Cross-Platform Educational Agent Benchmarking with Multimodal Language Models, a cross-platform educational agent benchmarking
Task
✓=Supported, ×=Not supported. Cross-platform requires simultaneous multi-device operations.
framework based on knowledge enhancement and dual-graph evaluation. The overall framework is shown in Fig. 1.
Table I presents a comparison between KGCE and existing benchmark frameworks. Key features are categorized as: Interactive Environment (system’s operating context: Web/GUI/Code); Knowledge (structured knowledge management with knowledge graphs or dynamic reasoning supported by ✓); Cross-platform (concurrent multi-device operations requiring OS/device interoperability); Evaluation (Goal-based: final state verification; Trajectory: action sequence alignment; Graph-based: DAG checkpoint validation); Task Construction (Template: predefined patterns; Manual: human-crafted; Sub-task Comp: modular composition);Educational Task (curriculum integration or pedagogical assessment via ✓).
The main contributions are as follows:
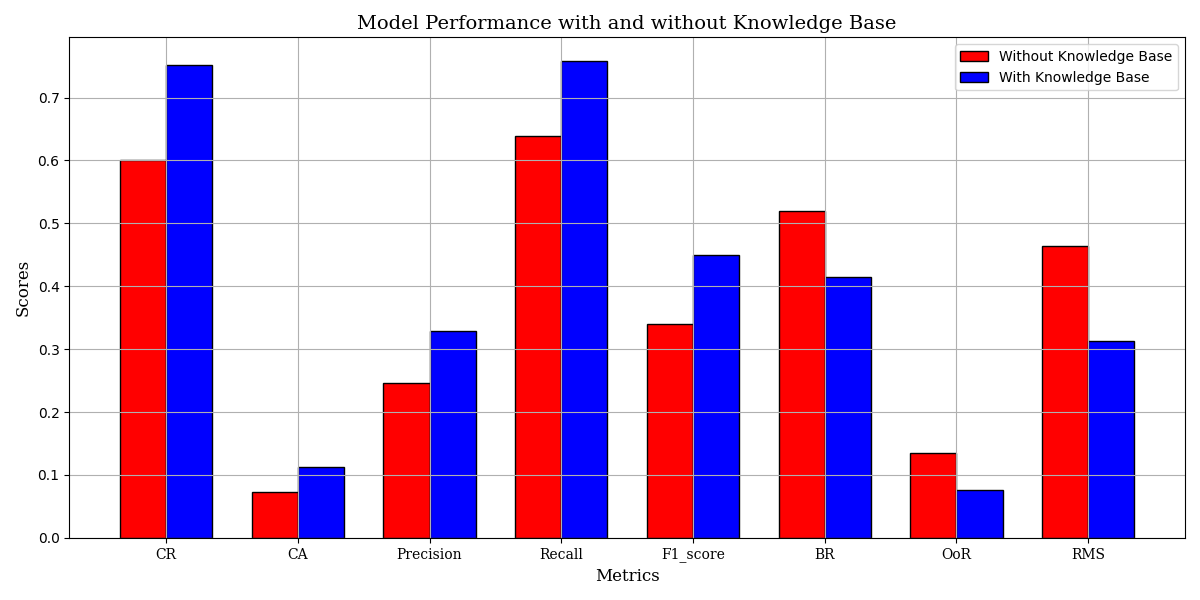
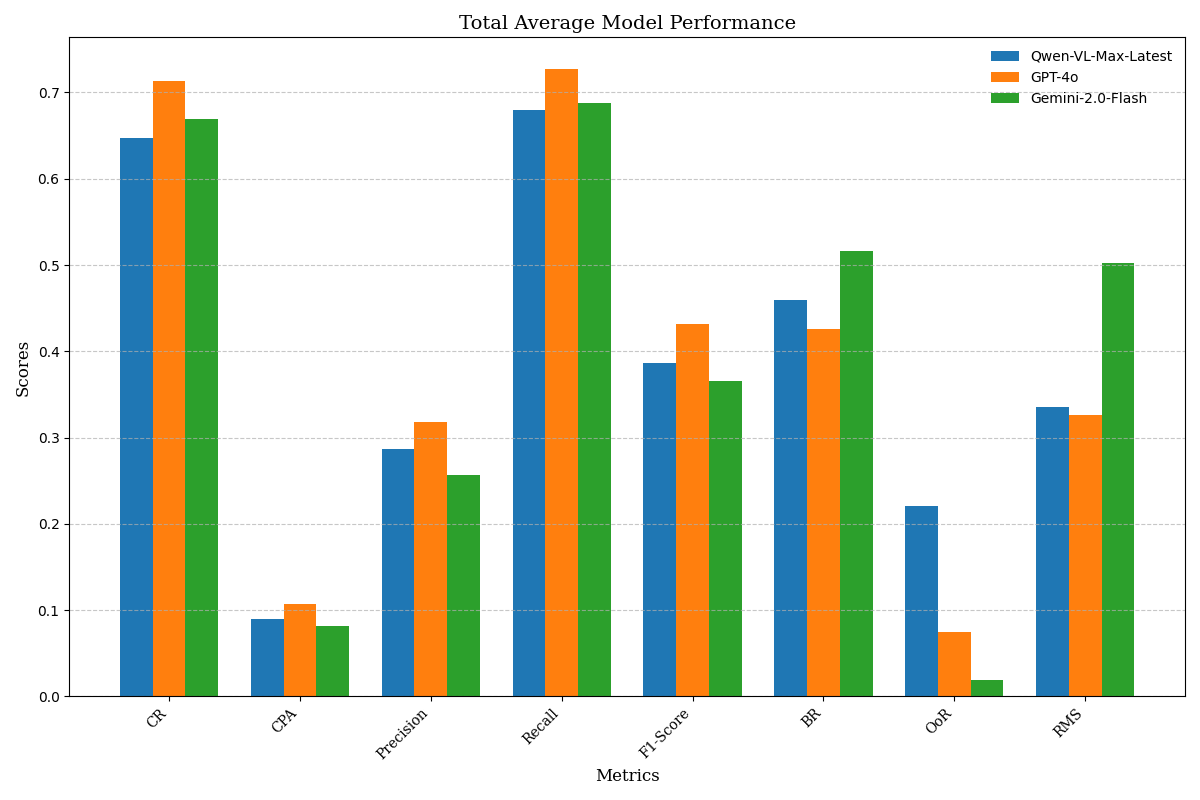
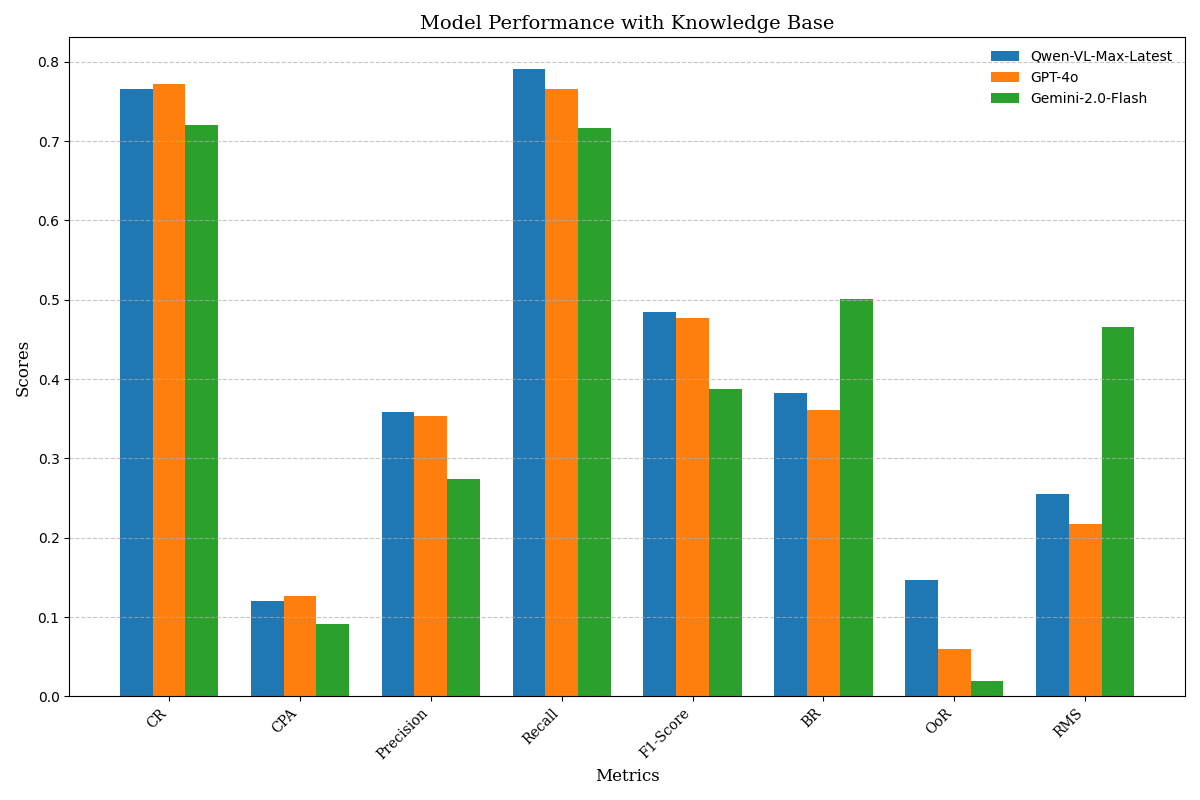
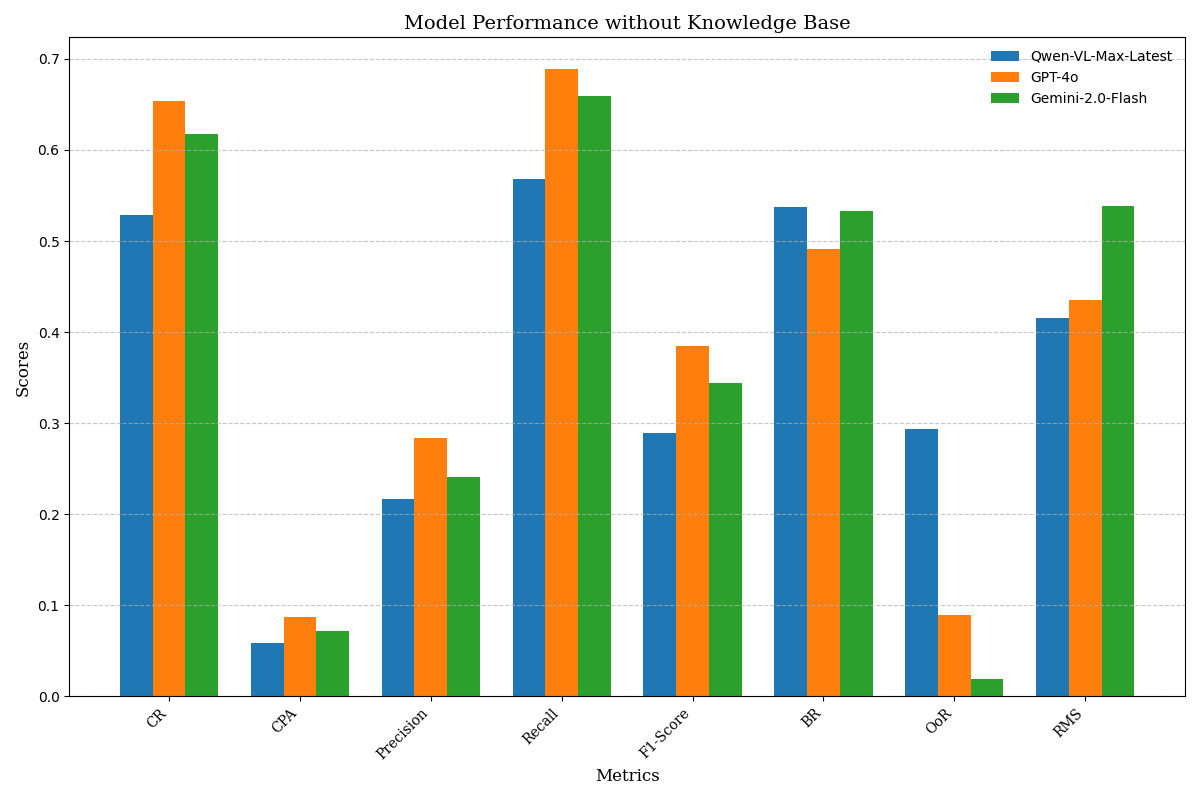
• We constructed a dataset of 104 educational tasks spanning Windows, Android, and cross-platform collaboration. These tasks involve operations with private-domain software and multi-device coordination workflows, and its dependencies are modeled using a DAG. This framework introduces eight fine-grained metrics to assess task performance in detail. • We validate the effectiveness of the knowledge base across several models, including Qwen-VL-Max-Latest, GPT-4o, and Gemini-2.0-Flash, revealing differences in their dependence on domain-specific knowledge.
To comprehensively contextualize our research, we structure the related work into four key dimensions: (1) crossplatform agents driven by large models, (2) task modeling and agents in educational scenarios, (3) knowledgeenhanced agent architectures, (4) agent evaluation method-ologies. These dimensions were selected because they collectively address the challenges of building intelligent agents in educational environments. By analyzing these aspects, we aim to highlight the gaps in existing research and position our contributions accordingly.
In recent years, MLMs have demonstrated significant potential in the field of cross-platform agents. CRAB introduced the first benchmark frame
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.