Let It Flow: Agentic Crafting on Rock and Roll, Building the ROME Model within an Open Agentic Learning Ecosystem
📝 Original Info
- Title: Let It Flow: Agentic Crafting on Rock and Roll, Building the ROME Model within an Open Agentic Learning Ecosystem
- ArXiv ID: 2512.24873
- Date: 2025-12-31
- Authors: Weixun Wang, XiaoXiao Xu, Wanhe An, Fangwen Dai, Wei Gao, Yancheng He, Ju Huang, Qiang Ji, Hanqi Jin, Xiaoyang Li, Yang Li, Zhongwen Li, Shirong Lin, Jiashun Liu, Zenan Liu, Tao Luo, Dilxat Muhtar, Yuanbin Qu, Jiaqiang Shi, Qinghui Sun, Yingshui Tan, Hao Tang, Runze Wang, Yi Wang, Zhaoguo Wang, Yanan Wu, Shaopan Xiong, Binchen Xu, Xander Xu, Yuchi Xu, Qipeng Zhang, Xixia Zhang, Haizhou Zhao, Jie Zhao, Shuaibing Zhao, Baihui Zheng, Jianhui Zheng, Suhang Zheng, Yanni Zhu, Mengze Cai, Kerui Cao, Xitong Chen, Yue Dai, Lifan Du, Tao Feng, Tao He, Jin Hu, Yijie Hu, Ziyu Jiang, Cheng Li, Xiang Li, Jing Liang, Xin Lin, Chonghuan Liu, ZhenDong Liu, Zhiqiang Lv, Haodong Mi, Yanhu Mo, Junjia Ni, Shixin Pei, Jingyu Shen, XiaoShuai Song, Cecilia Wang, Chaofan Wang, Kangyu Wang, Pei Wang, Tao Wang, Wei Wang, Ke Xiao, Mingyu Xu, Tiange Xu, Nan Ya, Siran Yang, Jianan Ye, Yaxing Zang, Duo Zhang, Junbo Zhang, Boren Zheng, Wanxi Deng, Ling Pan, Lin Qu, Wenbo Su, Jiamang Wang, Wei Wang, Hu Wei, Minggang Wu, Cheng Yu, Bing Zhao, Zhicheng Zheng, Bo Zheng
📝 Abstract
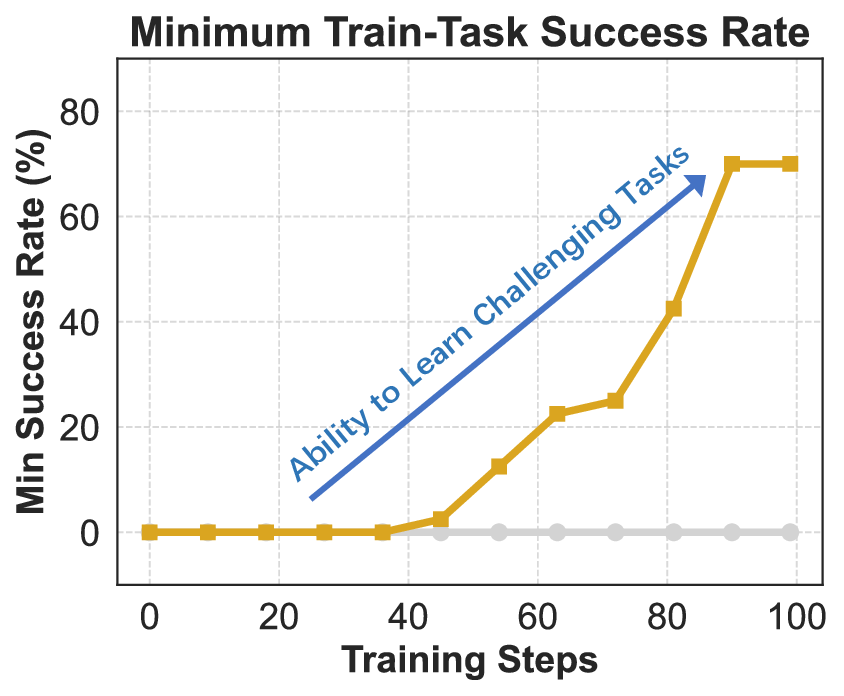
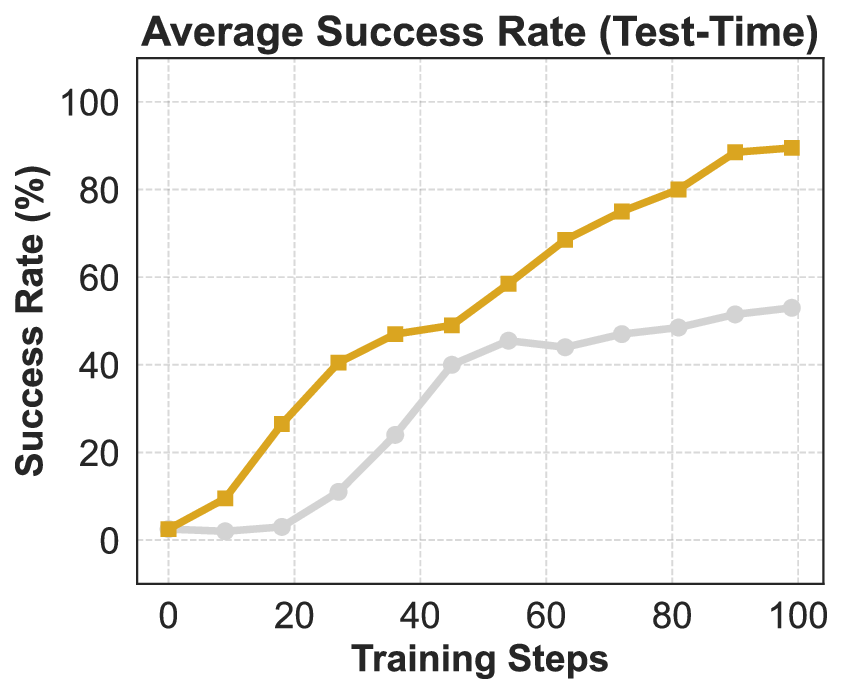
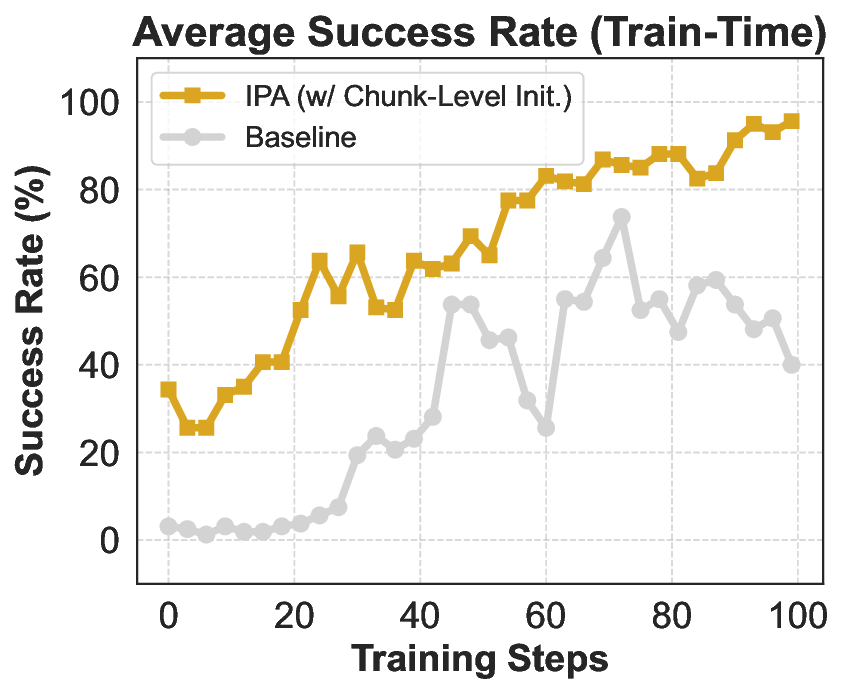
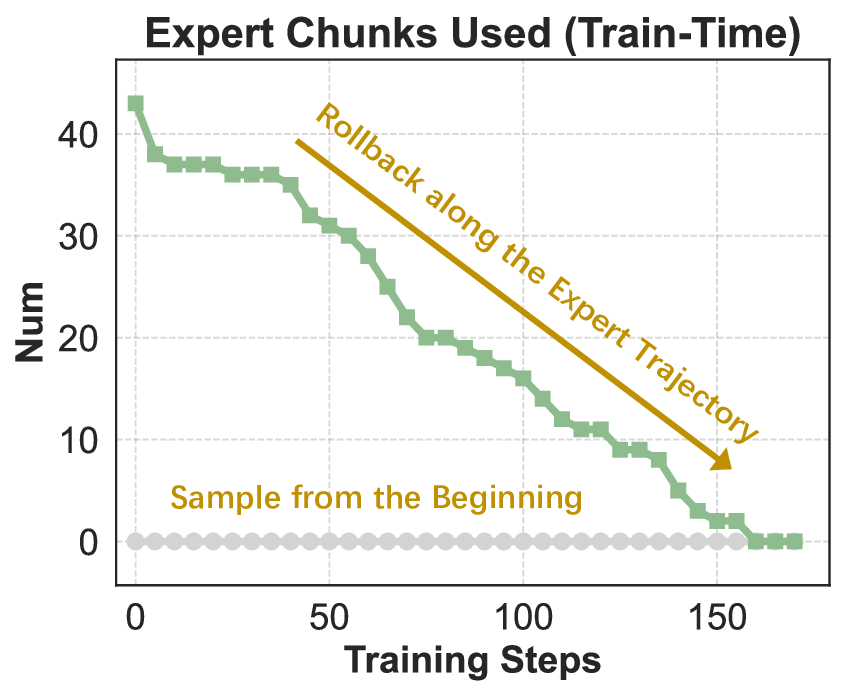
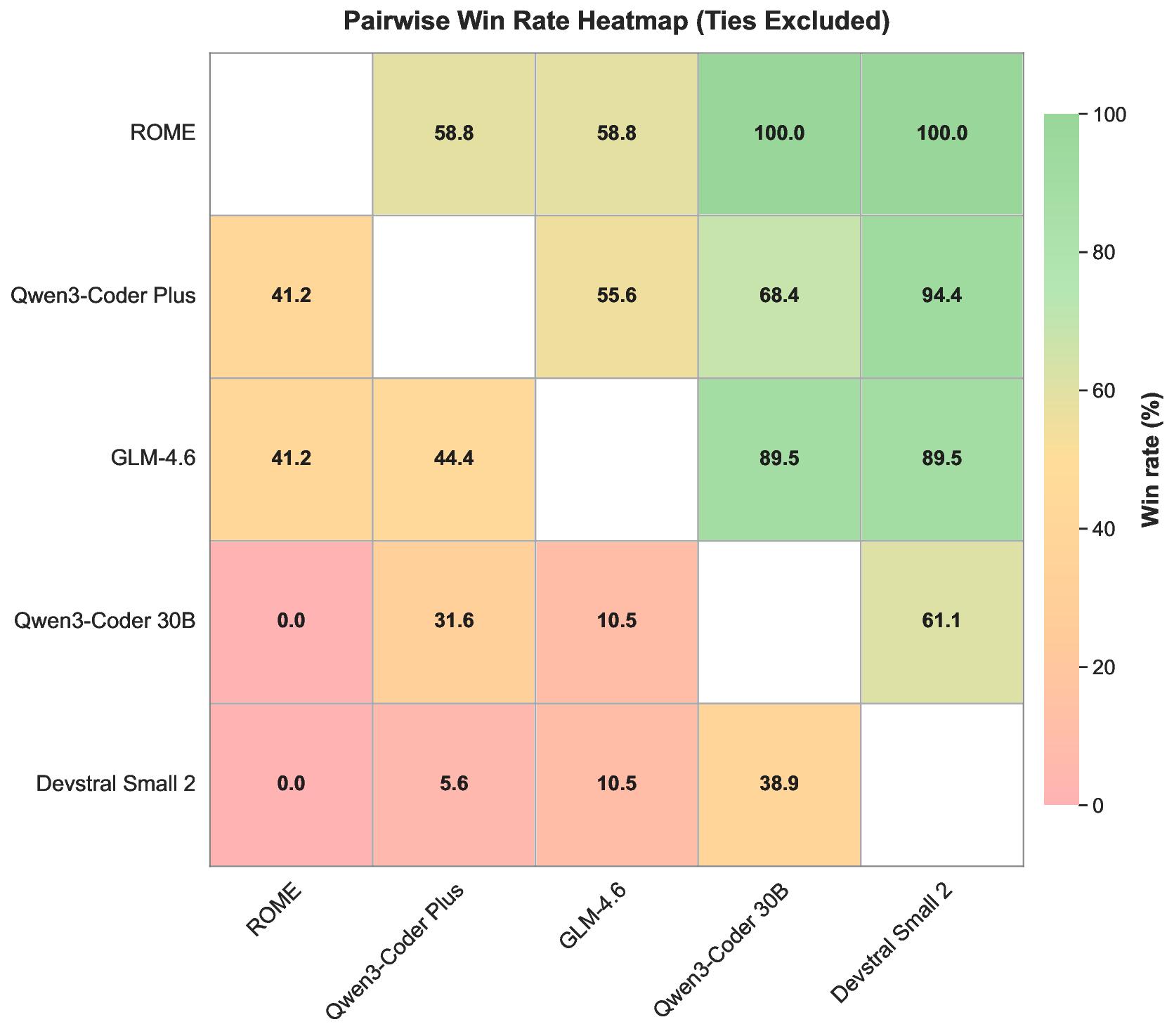
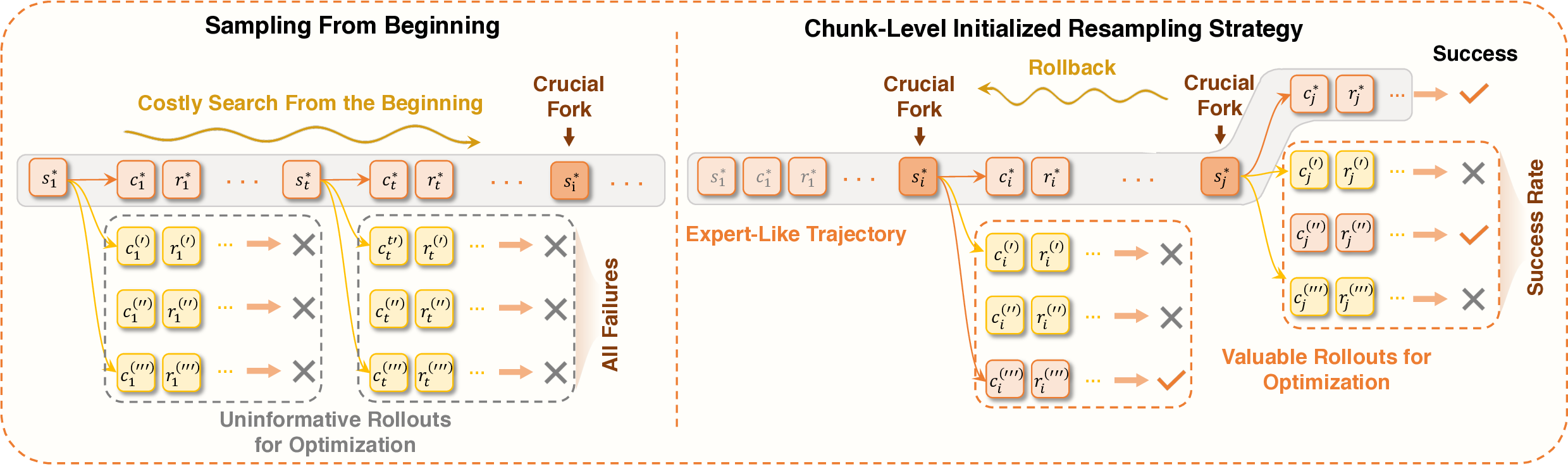
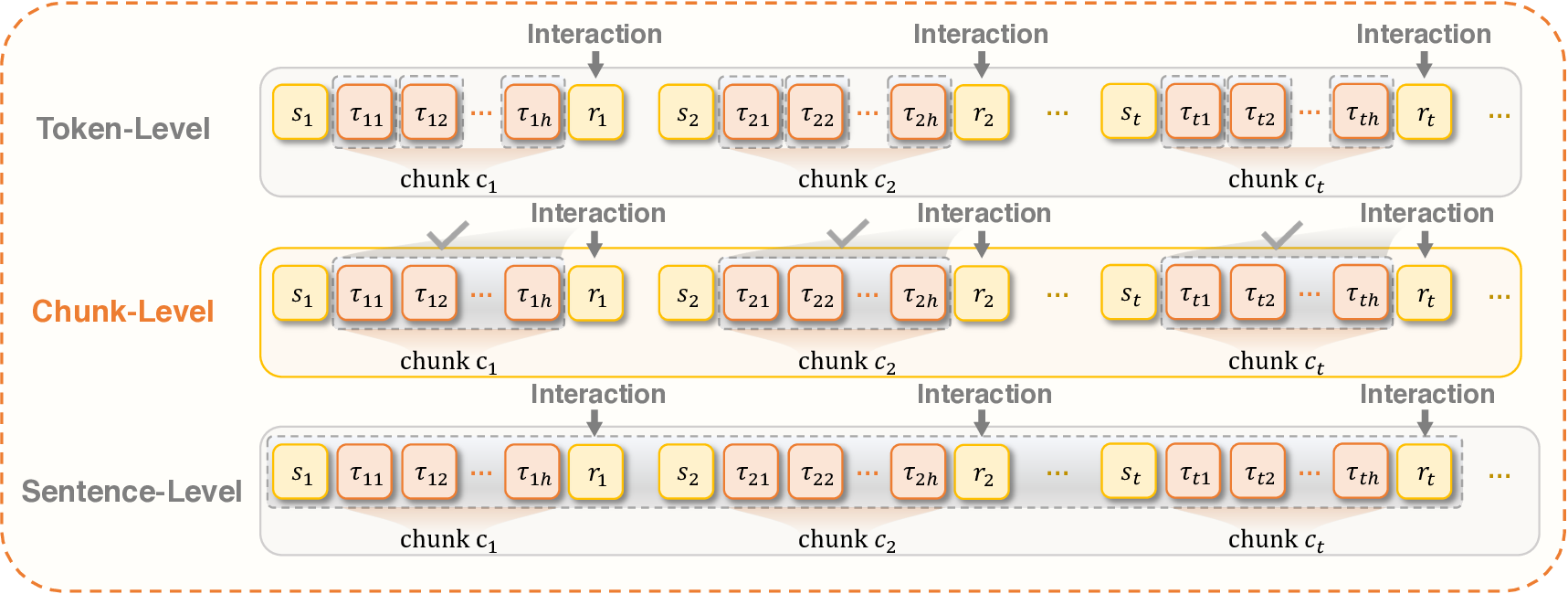
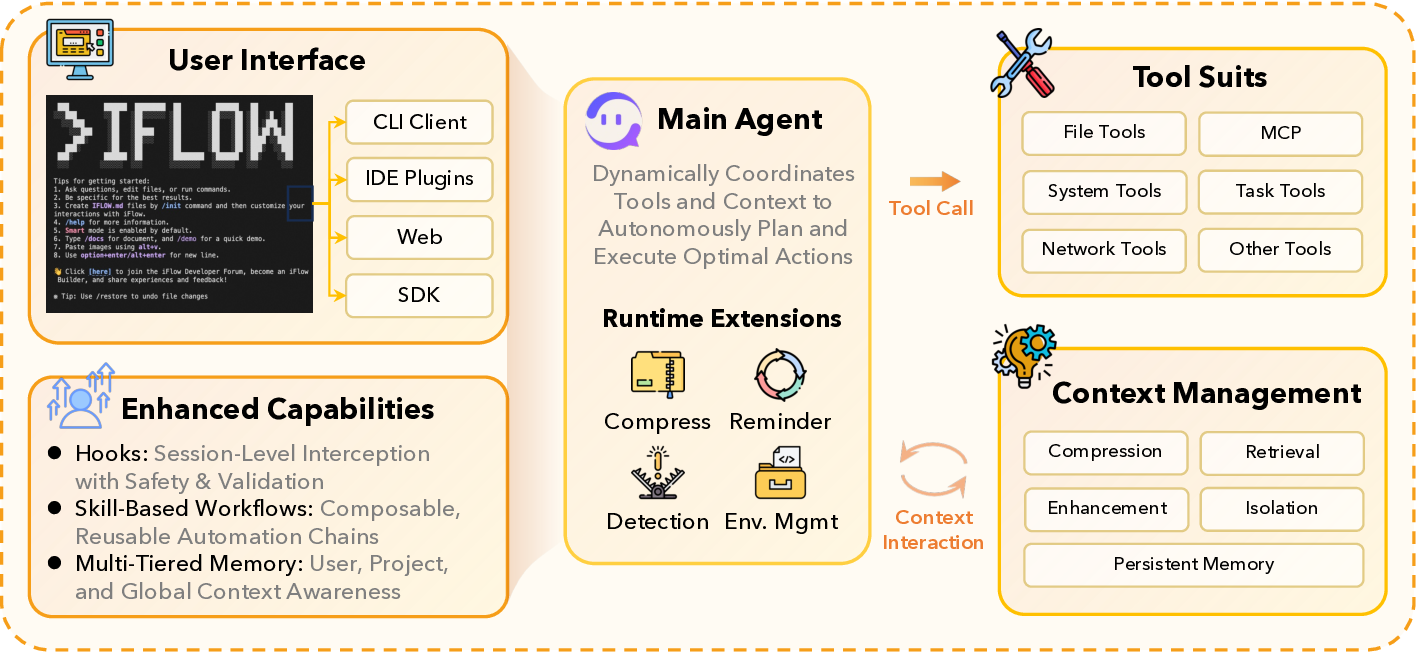
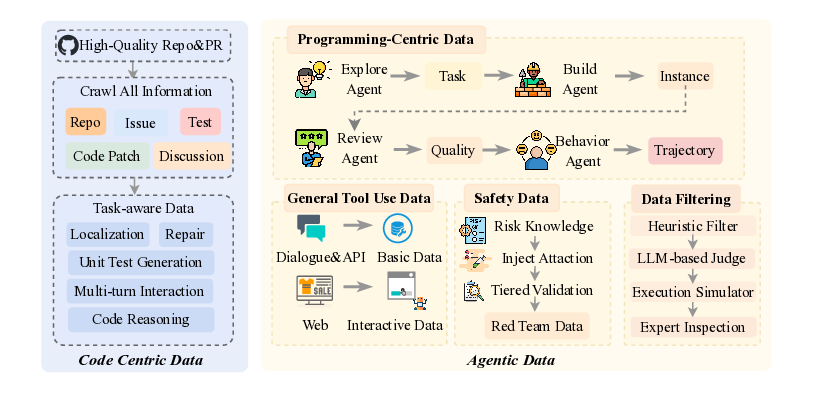
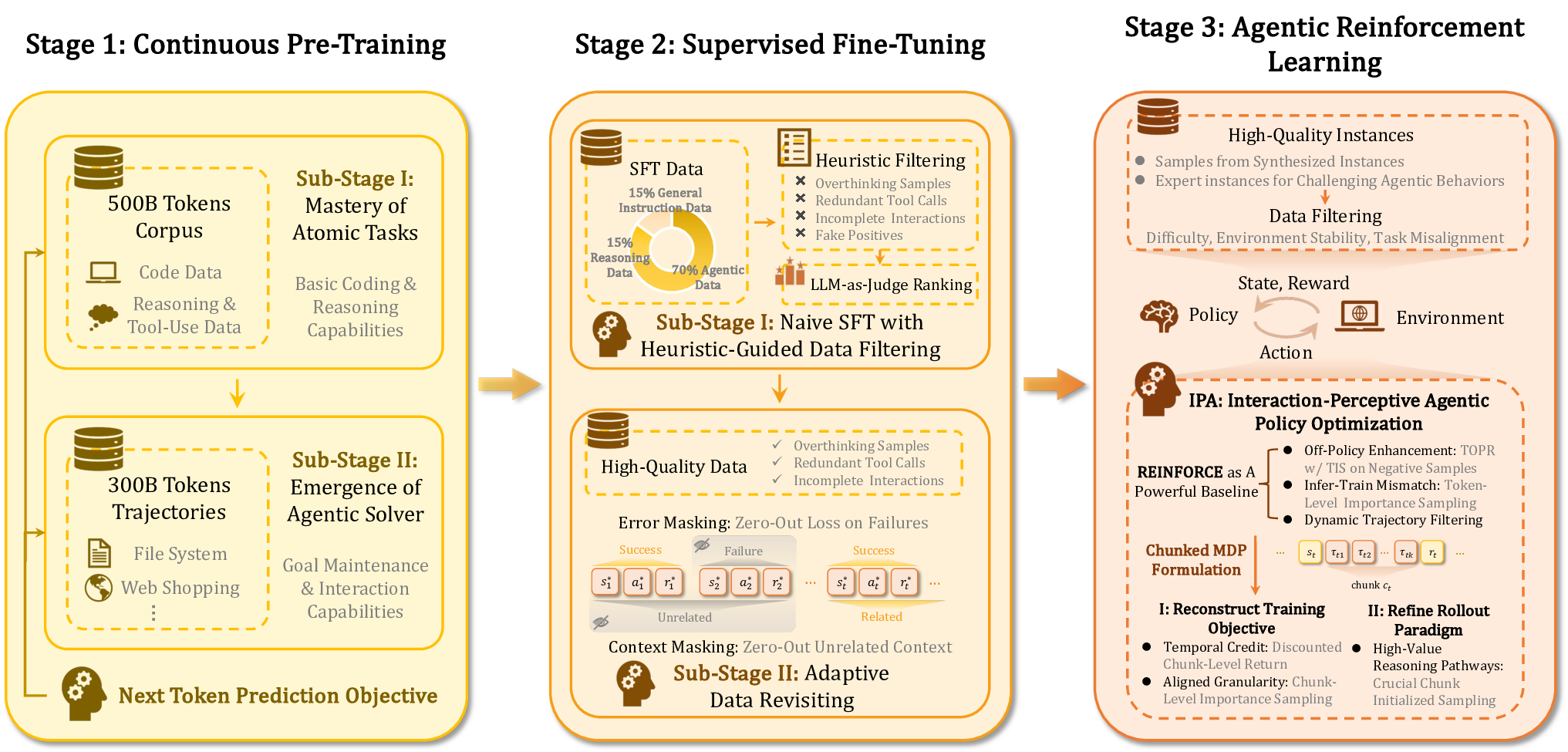
Agentic crafting, unlike one-shot response generation for simple tasks, requires LLMs to operate in real-world environments over multiple turns-taking actions, observing outcomes, and iteratively refining artifacts until complex requirements are satisfied. Yet the spirit of agentic crafting reaches beyond code, into broader tool-and languagemediated workflows where models must plan, execute, and remain reliable under interaction. Reaching this new regime demands sustained, painstaking effort to build an agentic ecosystem as the foundational bedrock, ultimately culminating in an agent model as the capstone. ROME wasn't built in a day. A principled, end-to-end agentic ecosystem can streamline the development of the agent LLMs from training to production deployment, accelerating the broader transition into the agent era. However, the opensource community still lacks such an ecosystem, which has hindered both practical development and production adoption of agents. To this end, we introduce the Agentic Learning Ecosystem (ALE), a foundational infrastructure that optimizes the end-to-end production pipeline for agent LLMs. ALE consists of three system components. ROLL is a post-training framework for weight optimization. ROCK is a sandbox environment manager that orchestrates environments for trajectory generation. iFlow CLI is an agent framework that enables configurable and efficient context engineering for environment interaction. We release ROME (ROME is Obviously an Agentic ModEl), an open-source agent grounded by ALE and trained on over one million trajectories. In addition, we curate a suite of data composition protocols that synthesize data spanning isolated, static snippets to dynamic, complex agentic behaviors, with built-in verification of safety, security, and validity. We further develop an end-to-end training pipeline and propose a novel policy optimization algorithm IPA, which assigns credit over semantic interaction chunks rather than individual tokens, improving training stability over long horizons. Empirical evaluations show that ROME achieves strong results across mainstream agentic benchmarks, including 24.72% on Terminal-Bench 2.0 and 57.40% accuracy on SWE-bench Verified, outperforming similarly sized models and rivaling those with over 100B parameters. To enable more rigorous evaluation, we introduce Terminal Bench Pro, a benchmark with improved scale, domain coverage, and contamination control. ROME still demonstrates competitive performance among open-source models of similar scale and has been successfully deployed in production, demonstrating the practical effectiveness of the ALE.💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content
📸 Image Gallery






Reference
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.