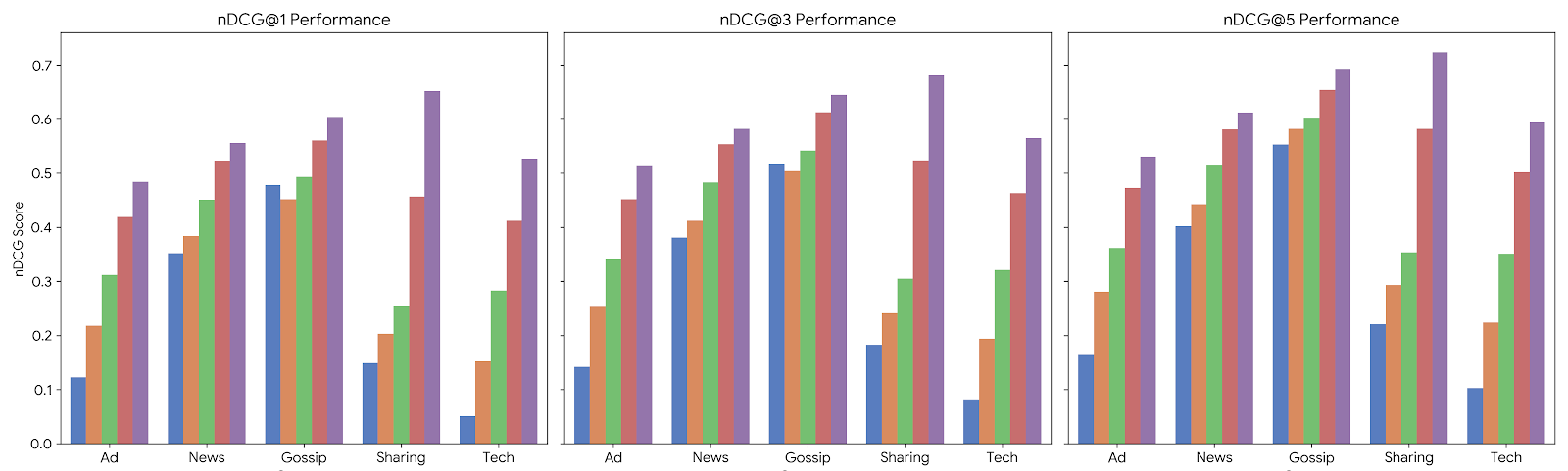
This research presents a cutting-edge recommendation system utilizing agentic AI for KYC (Know Your Customer in the financial domain), and its evaluation across five distinct content verticals: Advertising (Ad), News, Gossip, Sharing (User-Generated Content), and Technology (Tech). The study compares the performance of four experimental groups, grouping by the intense usage of KYC, benchmarking them against the Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (nDCG) metric at truncation levels of 𝑘 = 1, 𝑘 = 3, and 𝑘 = 5. By synthesizing experimental data with theoretical frameworks and industry benchmarks from platforms such as Baidu and Xiaohongshu, this research provides insight by showing experimental results for engineering a large-scale agentic recommendation system.
The transition from chronological feeds to algorithmically ranked experiences represents the most significant shift in digital media consumption of the last decade. As content production scales exponentially, the human capacity for consumption remains fixed, creating a "zero-sum" attention economy. In this environment, the Recommendation System (RecSys) serves as the primary gatekeeper. Early iterations of these systems relied on simple heuristic filters-popularity or recency. However, as user bases grew diverse and content libraries expanded into the billions, these rudimentary methods failed to address the "Long Tail" [4] of user interests and the nuanced semantic differences between content types.
Current mainstream recommender systems [6] typically employ a multi-stage, multi-model hybrid architecture to handle largescale content [5]. For example, Instagram’s Explore system uses a multi-stage pipeline of “recall -coarse ranking -fine rankingre-ranking”. In the recall stage, it uses a two-tower neural network model to generate vector embeddings for users and content, processing user features and content features separately before and after, thereby quickly finding candidate content through nearest neighbor search. This approach is similar to industry practices such as those of Facebook and Google, which simultaneously optimize multiple objectives such as click-through rate and retention rate by sharing expert subnetworks and task-specialized gated networks (MMoE) [11]. Google’s research indicates that multi-task learning (such as MMoE) can significantly improve the coordination between different objectives in recommender systems.
While the multi-stage architectures described in the abstract represent the current state-of-the-art (SOTA) in passive ranking, the field is undergoing a paradigm shift toward Agentic AI. Traditional recommendation systems function as sophisticated filters-they reactively rank existing content based on historical probability. In contrast, an Agentic Recommendation System is goal-directed, autonomous, and capable of complex reasoning. It does not merely “predict” what you might click; it “plans” a content consumption path to achieve a specific outcome (e.g., learning a new skill, entertainment, or purchasing decision).
In this transition, KYC (Know Your Customer) [7] evolves from a static compliance requirement into the dynamic “memory” and “context” module of an AI Agent.
This report analyzes how varying levels of KYC depth-from Cold Start [10] (No Context) to Deep Personalized Context (Full KYC in this work), impact the performance metrics (nDCG) across different content domains, serving as a roadmap for building the next generation of Agentic Recommendation System [9].
Recommendation system introduced in this research is designed around multimodal fusion, cross-domain learning, and agentic AI orchestration, with a strong foundation in KYC-driven user understanding. The goal is to deliver both accurate personalization and high-quality exploration beyond users’ habitual information boundaries.
The system further leverages social graph information, modeling follow relationships as a heterogeneous graph that includes individual users, creators, and enterprise accounts. Using Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) for cross-domain recommendation, the algorithm propagates interest signals across connected nodes. This graph-based learning allows diversity and novelty to flow from high-activity users and creators to adjacent users, helping to overcome entrenched consumption patterns. As a result, the system enables both “crowd breaking” (exposing users to new communities) and “content breaking” (surfacing content outside users’ historical domains), without sacrificing relevance.
Recommendation System with Contextual and Social Graph Fusion
The system integrates multimodal deep representation techniques, such as computer vision and NLP models, to extract visual features and semantic tags from content, aligning image and short video features with the user’s interest space (visual semantic embedding) [2][1]. These multimodal features, along with social graph signals, are input into the ranking model, enabling the recommendation algorithm to perform cross-content domain association matching (cross-domain fusion), mapping a user’s interests in one domain to related content in other domains. For example, images and text content liked by a user are encoded as vectors to find works from other domains with similar themes in the vector space. Combining these mechanisms, the system aims to break through single interest circles and achieve “breaking the circle” recommendation: that is, while ensuring recommendation relevance, it introduces a certain proportion of unexpected content that matches the user’s potential preferences. To this end, in addition to directly using user embeddings to recall content from familiar domains during candidate generation, the system also employs a combination of coll
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.