Accurately forecasting daily exchange rate returns represents a longstanding challenge in international finance, as the exchange rate returns are driven by a multitude of correlated market factors and exhibit high-frequency fluctuations. This paper proposes EXFormer, a novel Transformer-based architecture specifically designed for forecasting the daily exchange rate returns. We introduce a multi-scale trend-aware self-attention mechanism that employs parallel convolutional branches with differing receptive fields to align observations on the basis of local slopes, preserving long-range dependencies while remaining sensitive to regime shifts. A dynamic variable selector assigns time-varying importance weights to 28 exogenous covariates related to exchange rate returns, providing pre-hoc interpretability. An embedded squeeze-and-excitation block recalibrates channel responses to emphasize informative features and depress noise in the forecasting. Using the daily data for EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD, we conduct out-of-sample evaluations across five different sliding windows. EXFormer consistently outperforms the random walk and other baselines, improving directional accuracy by a statistically significant margin of up to 8.5--22.8%. In nearly one year of trading backtests, the model converts these gains into cumulative returns of 18%, 25%, and 18% for the three pairs, with Sharpe ratios exceeding 1.8. When conservative transaction costs and slippage are accounted for, EXFormer retains cumulative returns of 7%, 19%, and 9%, while other baselines achieve negative. The robustness checks further confirm the model's superiority under high-volatility and bear-market regimes. EXFormer furnishes both economically valuable forecasts and transparent, time-varying insights into the drivers of exchange rate dynamics for international investors, corporations, and central bank practitioners.
Exchange rates lie at the core of global finance, shaping trade, capital flows, monetary policy transmission, portfolio allocation, and corporate risk management [1]. Accurate day-ahead forecasts support hedging by multinational firms, guide central bank interventions, and inform systematic trading strategies used by hedge funds [2]. Yet despite decades of research, forecasting daily exchange rate returns remains one of the most persistent challenges in international finance [3,4]. Meese and Rogoff [5] demonstrated that structural and time-series models routinely fail to outperform a simple random walk in out-of-sample tests. The Meese-Rogoff puzzle reflects two fundamental difficulties. First, daily returns combine high-frequency noisemicrostructure effects, news-driven volatility, liquidity shocks-with slower patterns such as medium-term cycles from interest differentials and carrytrade activity [6,7,8,9]. Second, it is necessary to model the influence and cross-market interactions of diverse exogenous drivers, such as other currency pairs, stock and commodity indices, and scheduled macroeconomic announcements on the daily returns behavior [10]. Traditional econometric models, especially those designed for lower-frequency data, often produce unstable daily forecasts and are prone to overfitting [11,12]. Portfoliobalance theory further highlights the role of cross-asset capital flows and time-varying risk preferences, which conventional models typically overlook [13]. The core research gap is thus how to jointly model multi-scale temporal dependencies and multi-factor cross-market linkages. Although uncovered interest parity (UIP) implies unpredictability of exchange rate changes, its persistent empirical rejection indicates the presence of time-varying risk premia that more advanced forecasting models may exploit [1,14].
Recent work increasingly applies machine learning and deep learning to forecasting daily exchange rate returns [15,16,17]. Classical methods such as SVMs and random forests offer limited gains, as they ignore temporal structure [18,19]. RNN-based models including LSTM and GRU networks, better capture sequential dependencies [20,21] and have been widely tested in financial forecasting (Fischer and Krauss [22]; Gu et al. [23]), yet still struggle with long-range patterns and with modeling complex non-local interactions across economic drivers [24]. Methodologically, many studies emphasize technical improvements without rigorous comparison to the random walk benchmark [25], and often report only statistical metrics.
Transaction-cost-adjusted evaluations remain scarce, leaving open whether model forecasts yield economically meaningful gains [26,14]. Determining whether any approach can outperform the random walk both statistically and economically remains a core question in daily exchange rate forecasting.
The emergence of Transformer-based architectures offers a promising alternative [27], but their direct application to financial time series faces three critical limitations. First, the standard pointwise self-attention mechanism, designed for discrete tokens, fails to capture the continuous, trend-like features of financial data [28,29]. Second, standard Transformers lack mechanisms to differentiate influential market drivers from redundant noise among correlated external factors [30,31]. Third, these models remain black boxes.
While post-hoc techniques like SHAP provide retrospective explanations, they fail to offer the forward-looking, time-varying interpretability required for adaptive investment decisions [32,33].
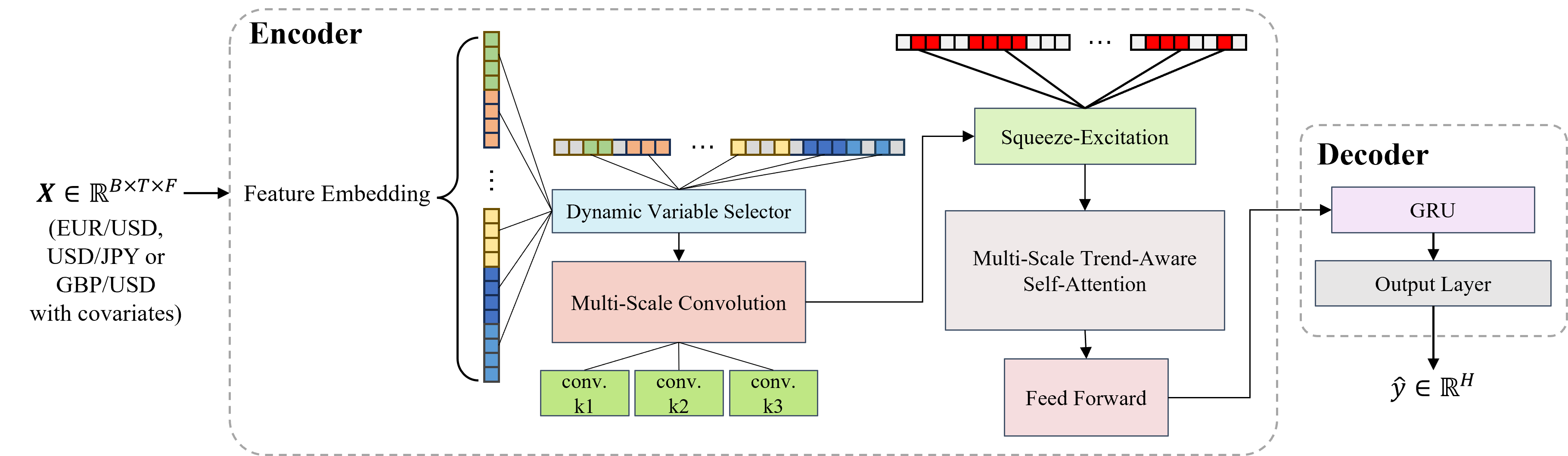
To address these challenges and gaps, we propose EXFormer, a novel Transformer-based architecture specifically engineered for forecasting the daily exchange rate returns. EXFormer introduces several critical innovations. At its core is a novel multi-scale trend-aware attention mechanism, which is designed to capture features across different time horizons while being sensitive to local trends. This is complemented by a squeeze-andexcitation (SE) block that learns to amplify the most informative feature channels while suppressing redundancy. To manage the complex web of external impact factors, we integrate a dynamic variable selector that learns daily importance weights for each covariate, allowing the model to focus on the most relevant market information and adapt as market conditions evolve. The encoder’s rich output representation is then passed to a decoder, which utilizes a GRU and a linear layer to generate the final returns forecast. Moreover, for interpretability, the dynamic variable selector provides a built-in pre-hoc explanation, assigning a specific weight to each covariate before the prediction is made, which allows for both global and time-varying interpretability, offering a granular view of how each variable’s importance evolves at every time step.
We evaluate EXFormer using daily data for three major currency pairs (EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD) alongside
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.