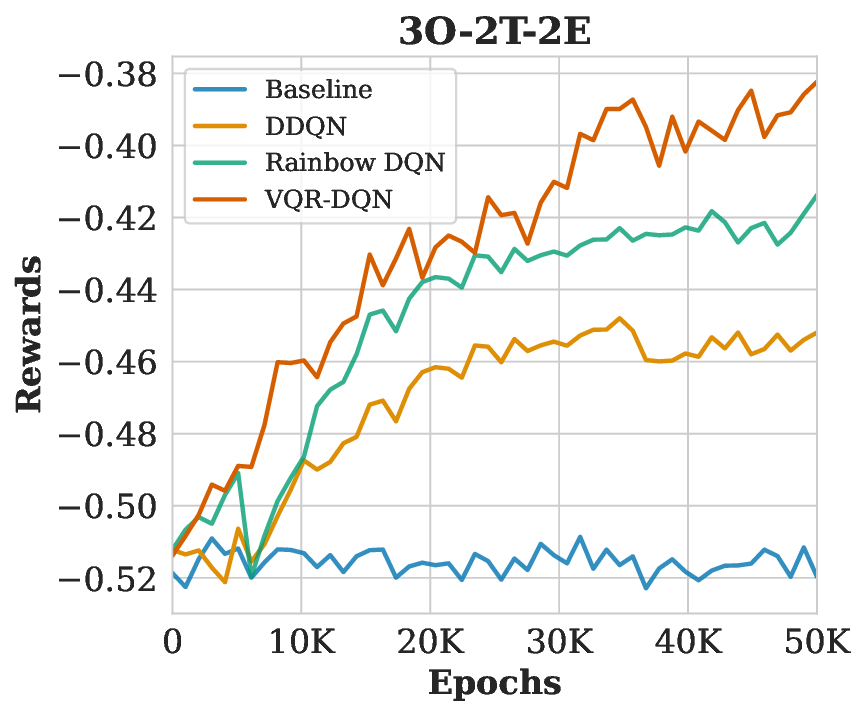
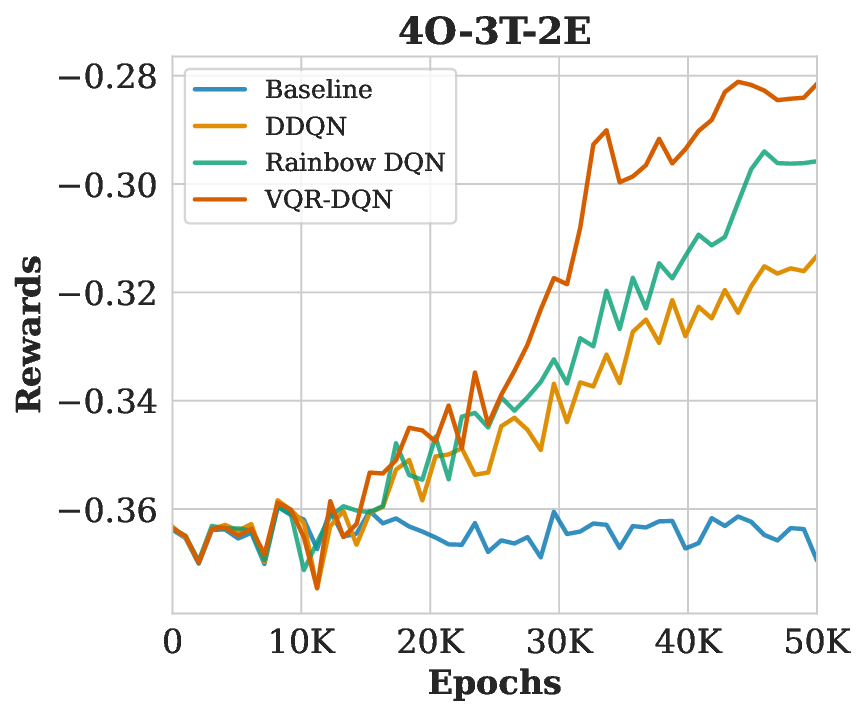
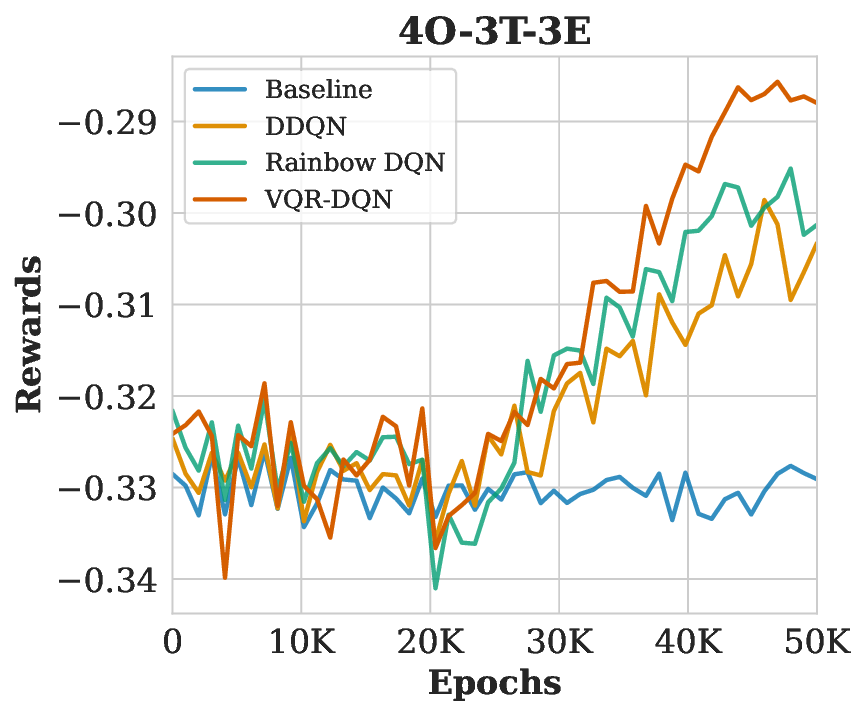
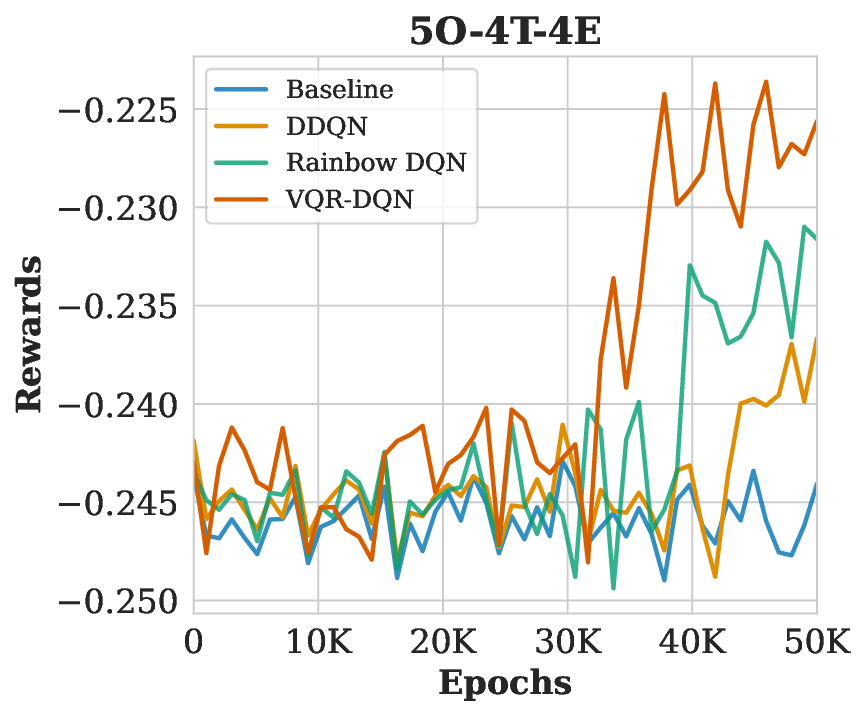
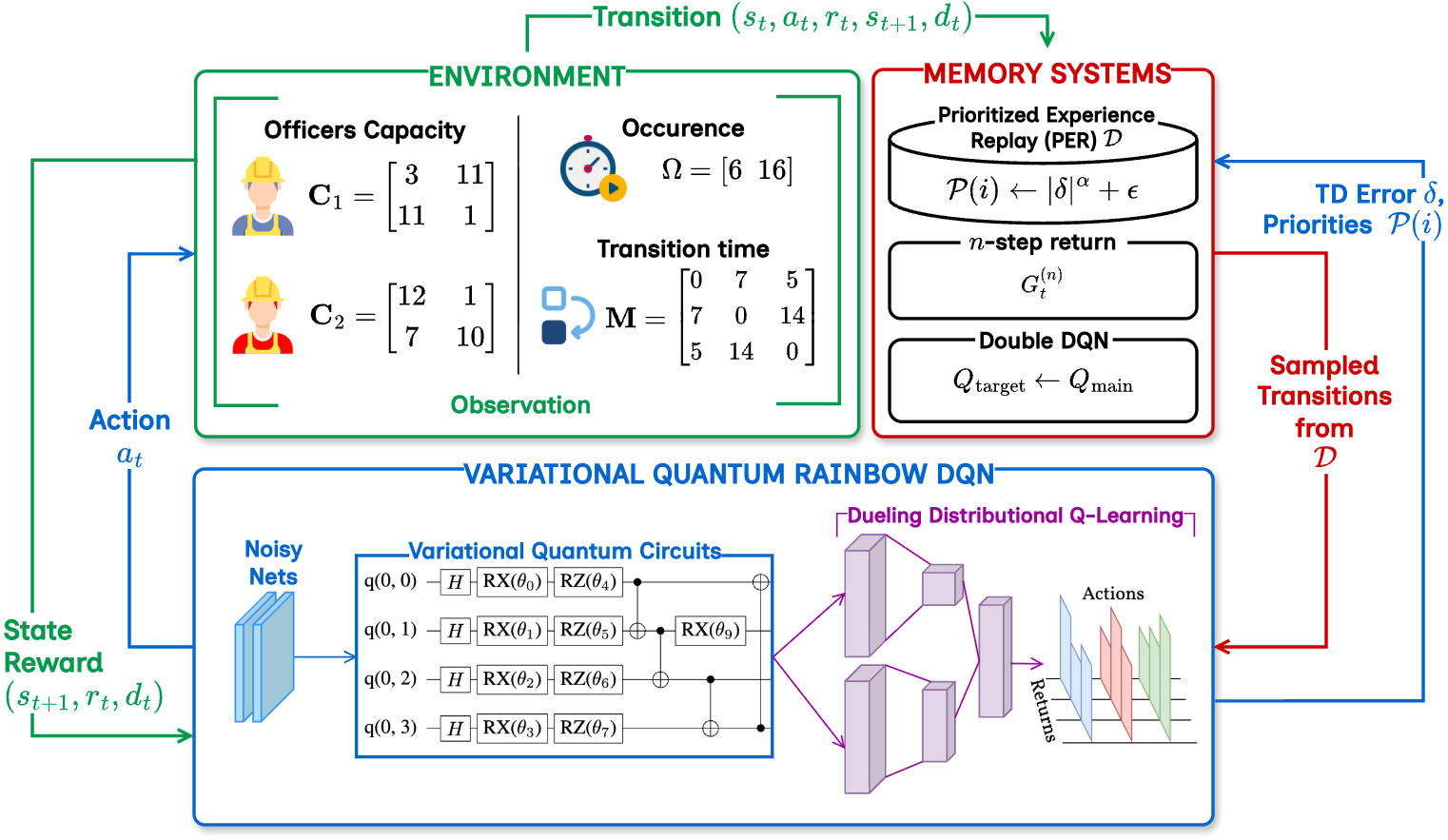
Resource allocation remains NP-hard due to combinatorial complexity. While deep reinforcement learning (DRL) methods, such as the Rainbow Deep Q-Network (DQN), improve scalability through prioritized replay and distributional heads, classical function approximators limit their representational power. We introduce Variational Quantum Rainbow DQN (VQR-DQN), which integrates ring-topology variational quantum circuits with Rainbow DQN to leverage quantum superposition and entanglement. We frame the human resource allocation problem (HRAP) as a Markov decision process (MDP) with combinatorial action spaces based on officer capabilities, event schedules, and transition times. On four HRAP benchmarks, VQR-DQN achieves 26.8% normalized makespan reduction versus random baselines and outperforms Double DQN and classical Rainbow DQN by 4.9-13.4%. These gains align with theoretical connections between circuit expressibility, entanglement, and policy quality, demonstrating the potential of quantum-enhanced DRL for large-scale resource allocation. Our implementation is available at: https://github.com/Analytics-Everywhere-Lab/qtrl/.
Resource allocation represents a fundamental NP-hard combinatorial optimization problem with diverse applications across software systems, including underwater resource management [43,4], human resource allocation [27,28], inventory allocation [36,37], and network resource distribution [19,2]. Various solution approaches have been developed due to the problem's complexity [29,13]. While exact classical methods succeed for small problem instances, real-world software engineering scenarios often involve high-dimensional optimization spaces where classical approaches encounter exponential time complexity, creating a critical performance bottleneck. This computational barrier has positioned quantum computing as a promising paradigm for addressing resource allocation challenges in modern software systems, leveraging quantum mechanical principles to explore solution spaces more efficiently than classical counterparts.
Reinforcement Learning (RL) has emerged as a promising approach for addressing these challenges. Deep Q-Networks (DQN) utilize neural networks to map state spaces to action Q-values, enabling optimal action selection [25]. The RL field has demonstrated impressive capabilities across games [32], continuous control [21], locomotion [30], navigation [8], and robotics [20], while showing effectiveness in solving optimization problems relevant to resource allocation [6]. Recent quantum computing advancements have introduced new possibilities, particularly through Quantum Reinforcement Learning (QRL). Quantum computing leverages superposition and entanglement to explore solution spaces infeasible for classical computers [35]. A key QRL approach utilizes Variational/Parameterized Quantum Circuits (VQCs/PQCs) [18,34], optimizable with classical ML techniques. VQCs function as quantum feature extractors, capturing complex data correlations challenging for classical models, thereby enhancing RL agent representation capabilities for improved decision-making in complex environments.
Hence, we introduce a QRL framework called the Variational Quantum Rainbow Deep Q-Network (VQR-DQN), integrating VQCbased quantum feature extraction with advanced RL techniques.
Our key contributions are: (1) VQR-DQN Framework: A novel architecture combining quantum-enhanced Ring-topology VQCs with Rainbow DQN [15], incorporating distributional 𝑄-learning, prioritized replay, and noisy networks. (2) Resource Allocation Environment: We demonstrate the VQR-DQN effectiveness via the Human Resource Allocation Problem (HRAP) as an MDP with a comprehensive environment design simulating real-world personnel dispatch scenarios. (3) Experimental Evaluation: Extensive experiments demonstrating VQR-DQN’s significant outperformance over Double DQN [38] and Rainbow DQN [15] in task completion time and resource utilization across varying HRAP complexity scenarios.
Resource allocation problem represents a long-standing problem in operations research and management science. Traditional approaches employ mathematical optimization techniques, i.e., Linear Programming (LP) [5], Mixed-Integer Linear Programming (MILP) [14], and branch-and-bound algorithms (B&B) [39], modeling allocation problems as linear equations with constraints. However, these methods are limited to small-scale problems due to exponential computational complexity growth. Heuristic and metaheuristic approaches, such as Genetic Algorithms (GA) [26], Simulated Annealing (SA) [22], and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) [17], provide approximate solutions for large-scale problems [7], yet suffer from domain-specific parameter tuning requirements and limited adaptability. RL has emerged as a promising resource allocation problem paradigm. Early applications used tabular approaches like Q-learning [41] for small state-action spaces. Deep RL (DRL) advancement enabled high-dimensional problem handling through DQN and variants, i.e., DDQN [38] and Dueling DQN [40], applied to this problem using neural networks for action-value function approximation [29,13]. Recent work [27] has integrated RL with search-based methods like Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS) [32], combining RL and heuristic search strengths for complex dynamic environments. Challenges remain in scaling RL methods to real-world resource allocation problems, particularly regarding high-dimensional state representations, policy robustness, and convergence efficiency.
QRL emergence has introduced new opportunities for complex optimization problems like HRAP. Primary advantages include handling exponentially large state-action spaces and simultaneous exploration of multiple solutions via quantum superposition and entanglement [24,11,9]. VQCs enhance agent environment understanding by extracting high-dimensional features difficult for classical methods. Recent research explores VQCs [18,34,1] as quantum feature extractors within RL frameworks, encoding classical data into quantum states and applying parameterized quantum gates to
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.