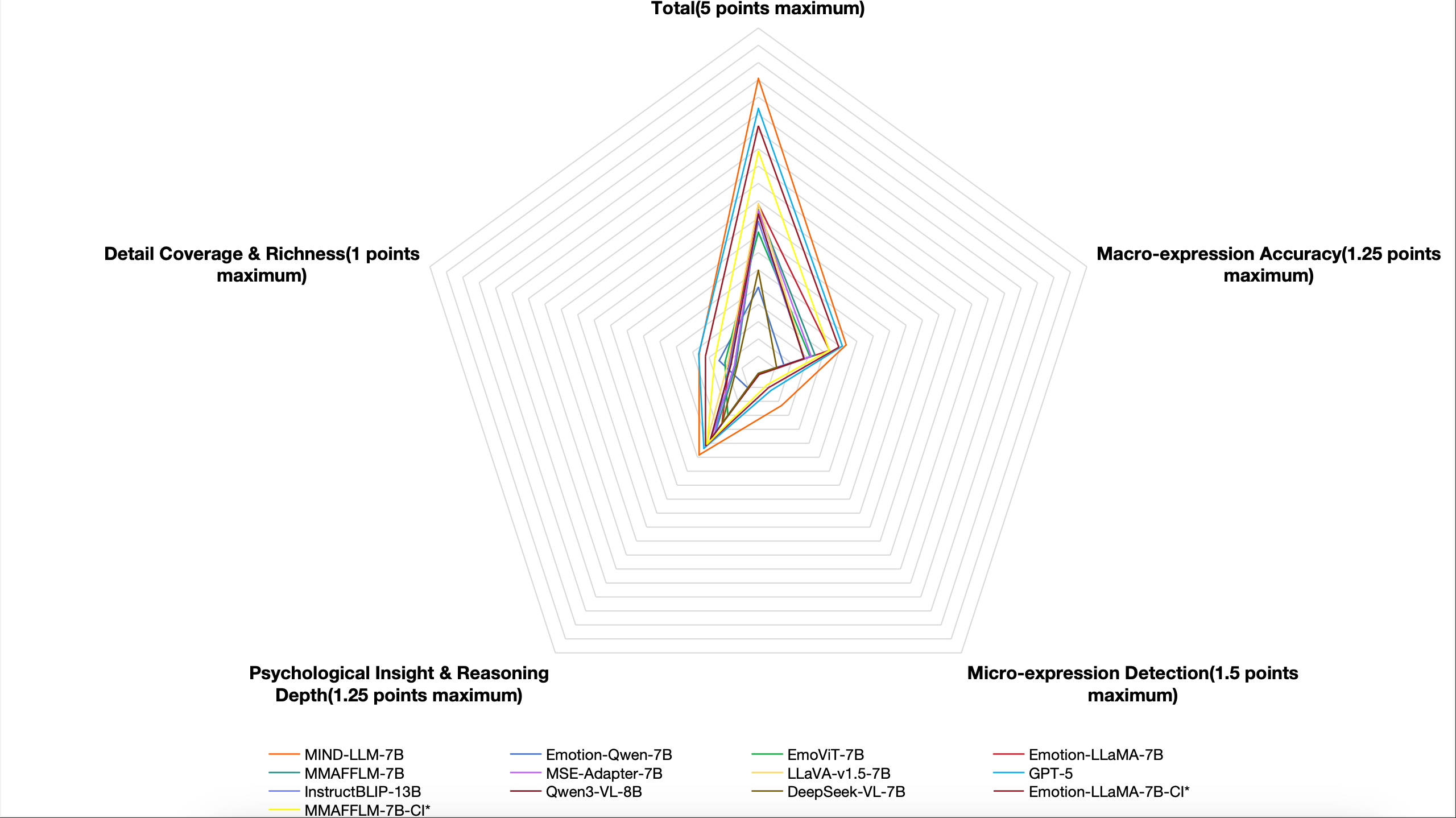
Generative psychological analysis of in-the-wild conversations faces two fundamental challenges: (1) existing Vision-Language Models (VLMs) fail to resolve Articulatory-Affective Ambiguity, where visual patterns of speech mimic emotional expressions; and (2) progress is stifled by a lack of verifiable evaluation metrics capable of assessing visual grounding and reasoning depth. We propose a complete ecosystem to address these twin challenges. First, we introduce Multilevel Insight Network for Disentanglement(MIND), a novel hierarchical visual encoder that introduces a Status Judgment module to algorithmically suppress ambiguous lip features based on their temporal feature variance, achieving explicit visual disentanglement. Second, we construct ConvoInsight-DB, a new large-scale dataset with expert annotations for micro-expressions and deep psychological inference. Third, Third, we designed the Mental Reasoning Insight Rating Metric (PRISM), an automated dimensional framework that uses expert-guided LLM to measure the multidimensional performance of large mental vision models. On our PRISM benchmark, MIND significantly outperforms all baselines, achieving a +86.95% gain in micro-expression detection over prior SOTA. Ablation studies confirm that our Status Judgment disentanglement module is the most critical component for this performance leap. Our code has been opened.
The aspiration to create artificial intelligence that genuinely understands human beings is a long-standing goal in computer science, holding the key to transformative applications from mental healthcare to trustworthy AI [8]. The true frontier for this endeavor lies not in controlled laboratory settings, but in the complex, unconstrained dynamics of "in-the-wild" conversations-the very scenarios where human understanding is most challenged, as psychological research like Truth-Default Theory (TDT) [17]suggests. It is in these low-stakes interactions where the only reliable clues to a person's inner state are often the most subtle, involuntary, and purely visual "emotional leakages" [33].
Capturing these visual signals is paramount, yet this presents a dual challenge. First, there is a critical technical obstacle in the visual domain which we term Articulatory-Affective Ambiguity. The same facial muscles used for emotional expression are also used for speech, creating profound ambiguity in a video-only analysis [32]. Current Vision-Language Models (VLMs) [6,12], with their holistic feature aggregation, are architecturally incapable of resolving this, frequently misinterpreting the visual patterns of articulation as affective signals, as shown in Figure 1. Second, and equally important, is a critical void in meaningful evaluation. While evaluation protocols are established for affective computing in controlled or semi-controlled settings, they are fundamentally ill-equipped for the fluid, context-dependent nature of in-the-wild dialogue. This leaves the community without a standardized and automated method to assess a generated psychological analysis for its visual grounding, logical depth, and descriptive richness in these challenging, realistic scenarios.
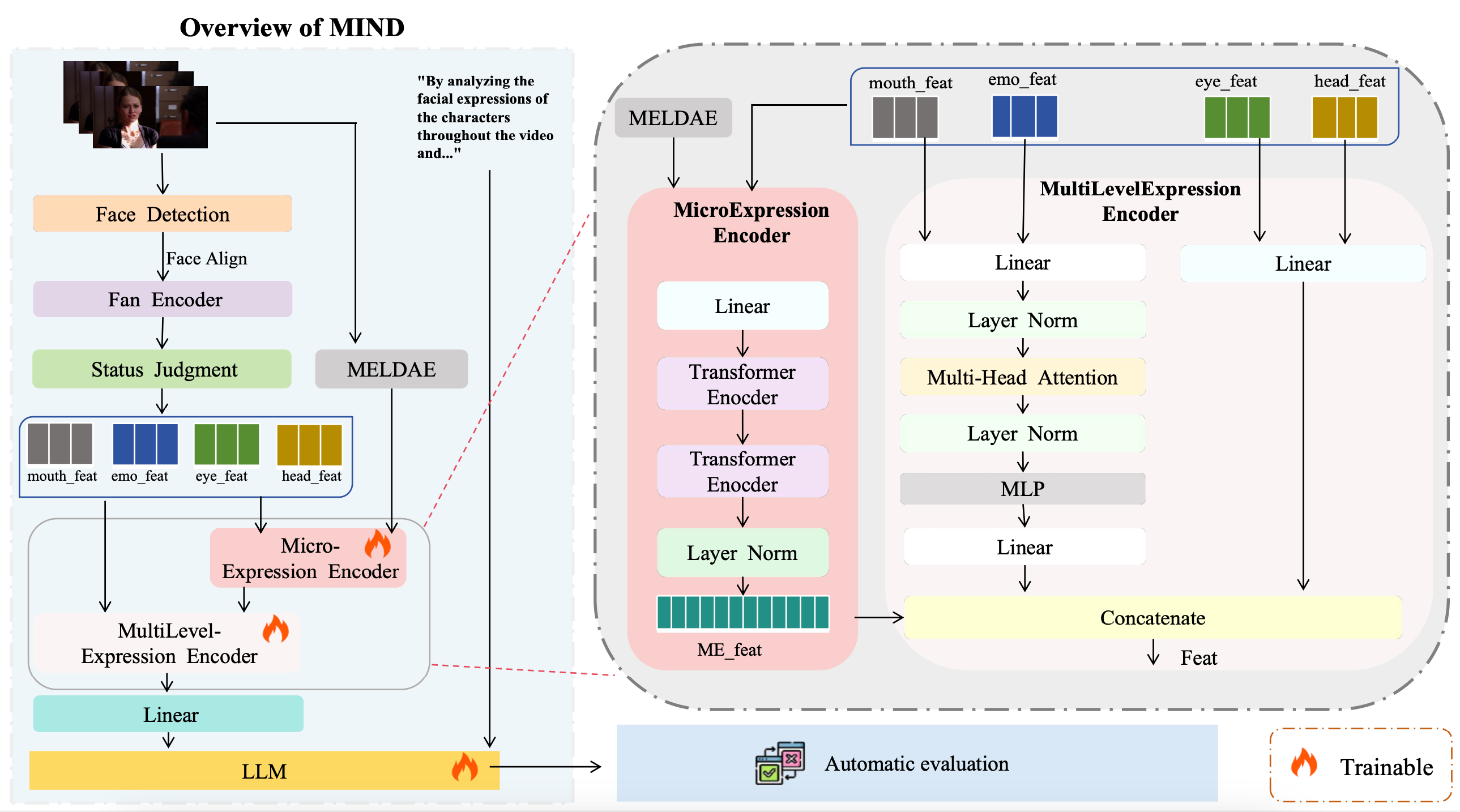
In this work, we tackle these twin challenges of modeling and evaluation head-on. We introduce Multilevel Insight Network for Disentanglement(MIND), a novel hierarchical vision-language architecture designed to explicitly disentangle the visual features of speech from those of emotion. Critically, to measure its true capabilities, we also propose what is, to our knowledge, the first automatic evaluation framework:Psychological Reasoning Insight Scoring Metric(PRISM) specifically designed for the multifaceted assessment of generative psychological analysis in in-the-wild conversational settings. By combining a sophisticated model with a bespoke, meaningful benchmark, we create a complete ecosystem for advancing research in this challenging domain.
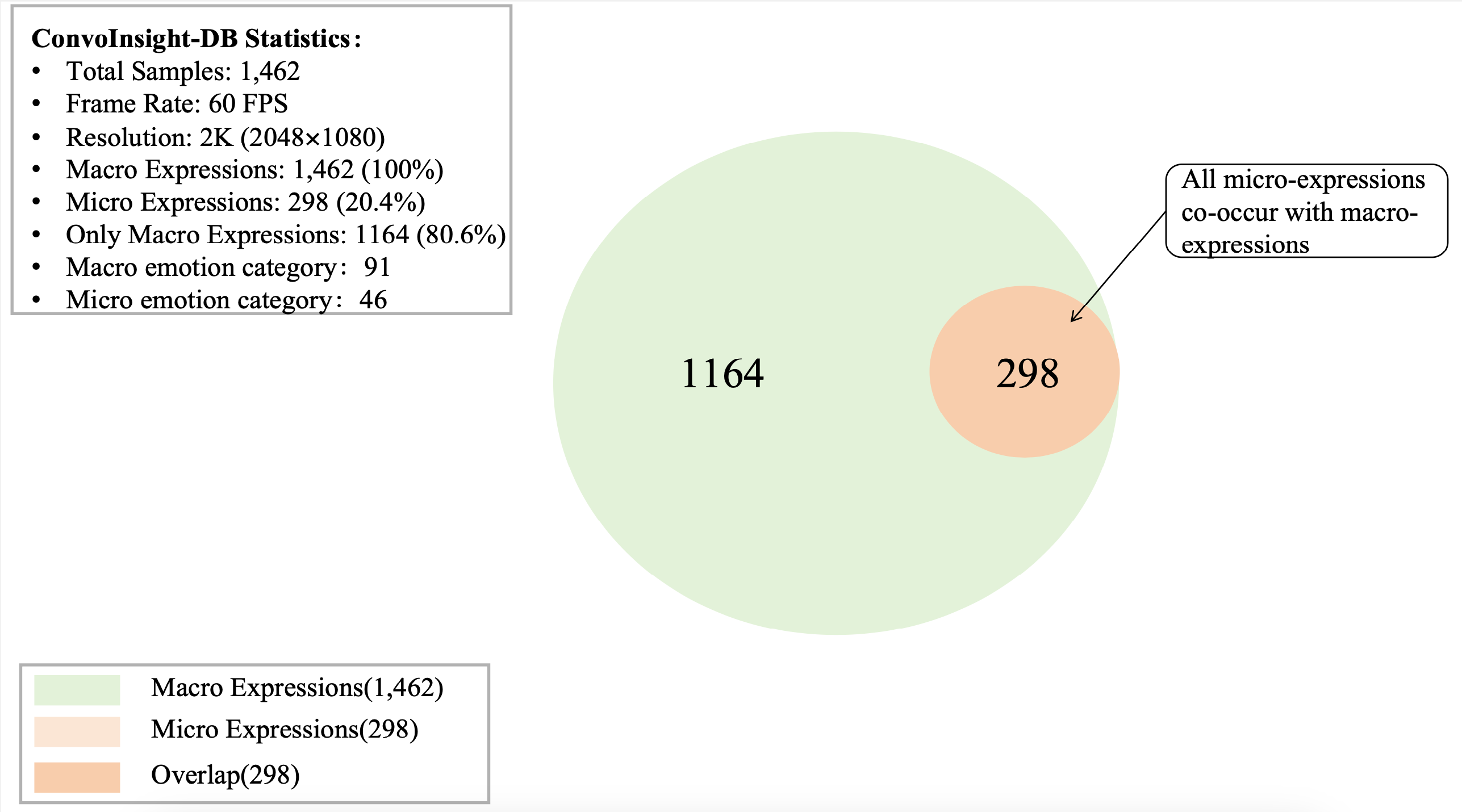
To summarize, we make the following contributions: (1) We propose MIND, a novel hierarchical framework that explicitly distinguishes articulatory movements from emotional signals. (2) We design and present a comprehensive evaluation framework, PRISM, which is the first of its kind for automatic, vision-based psychological analysis, particularly for natural conversation scenarios. (3) We construct a new dataset, ConvoInsight-DB, which features macro-expressions, micro-expressions, character emotion analysis, and character psychological analysis.
Our research is positioned at the confluence of VLMs and fine-grained Facial Affective Computing, addressing critical gaps in both representation learning and evaluation.
Vision-Language Models and Facial Affective Computing. The current paradigm in video understanding is dominated by large VLMs like Video-LLaMA [47] and Qwen2.5-VL [2], which couple a holistic visual encoder with a Large Language Model (LLM). Concurrently, the field of Facial Affective Computing has a rich history of developing specialized models for recognizing discrete emotions or detecting micro-expressions [1,34]. However, both lines of research fall short of our goal. VLMs are architecturally blind to the fleeting, localized facial cues, while traditional affective computing models are framed as recognition tasks, outputting mere labels rather than the rich, inferential generative analysis required to explain the ‘why’ behind an expression. Our work bridges this divide, reformulating the task from recognition to generative inference, enabled by a fine-grained visual encoder.
Disentangled Representation for Facial Analysis. The principle of learning disentangled representations has proven effective for separating static facial factors like identity from expression [41]. This body of work inspires our approach but has yet to address the core challenge of in-the-wild conversations: disentangling two dynamic, co-occurring, and visually ambiguous processes-the visual patterns of articulation and the subtle signals of affect. Therefore, to address
Granularity Mental activity Modality Macro-expression analysis Micro-expression detection Micro-expressions analysis
Table 1. Summary of existing popular benchmarks of sentiment analysis (representatively summarized, not fully covered).
this pain point, we designed the MIND visual network to decouple the visual features of pronunciation from the visual fe
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.