스킴 인식 대비 학습을 통한 효율적인 문서 표현
📝 원문 정보
- Title: Skim-Aware Contrastive Learning for Efficient Document Representation
- ArXiv ID: 2512.24373
- 발행일: 2025-12-30
- 저자: Waheed Ahmed Abro, Zied Bouraoui
📝 초록 (Abstract)
Transformer 기반 모델이 단어·문장 수준 과제에서 뛰어난 성능을 보이지만, 법률·의료와 같이 길이가 긴 문서를 효과적으로 표현하는 데는 한계가 있다. Sparse attention 메커니즘은 긴 입력을 처리할 수 있으나 연산 비용이 크고 전체 문맥을 충분히 포착하지 못한다. 계층적 Transformer는 효율성을 개선하지만, 문서의 서로 다른 섹션 간 관계를 명확히 설명하지 못한다. 인간은 텍스트를 스킴(요약) 방식으로 훑어 중요한 부분에 집중해 전체 의미를 파악한다. 이러한 인간의 전략을 모방하여, 우리는 섹션을 무작위로 마스킹하고, 자연어 추론(NLI) 기반 대비 학습 목표를 사용해 마스크된 섹션을 관련된 부분과 정렬하고 무관한 부분과는 거리두기 하는 자체 지도식 대비 학습 프레임워크를 제안한다. 이 방법은 인간이 정보를 종합하는 방식을 모방함으로써, 표현이 풍부하면서도 계산 효율이 높은 문서 임베딩을 만든다. 법률 및 생물의학 텍스트에 대한 실험 결과, 정확도와 효율성 모두에서 유의미한 향상을 확인하였다.💡 논문 핵심 해설 (Deep Analysis)
Paper Analysis
Title and Abstract Overview:
The paper titled “Skim-Aware Contrastive Learning for Efficient Document Representation” focuses on developing an efficient document encoder that can handle long documents effectively, inspired by how domain experts like legal or medical professionals skim through texts to identify key segments. The authors propose a Chunk Prediction Encoder (CPE) based on self-supervised contrastive learning.
Deep Analysis:
1. Motivation and Background: The introduction of language models in NLP has shifted the focus towards sentence and paragraph-level tasks using large pre-trained language models. However, there is a growing need for efficient document representation encoders for applications such as document classification, ranking systems, RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) systems, and specific domains like legal or medical fields.
2. Challenges in Document Representation Learning: Document representation learning faces challenges due to the increasing computational complexity with longer input lengths. Traditional models like BERT are inefficient for long documents because of their quadratic scaling. To address this, architectures such as Linformer, Big Bird, Longformer, and hierarchical transformers have been developed to handle long inputs more efficiently.
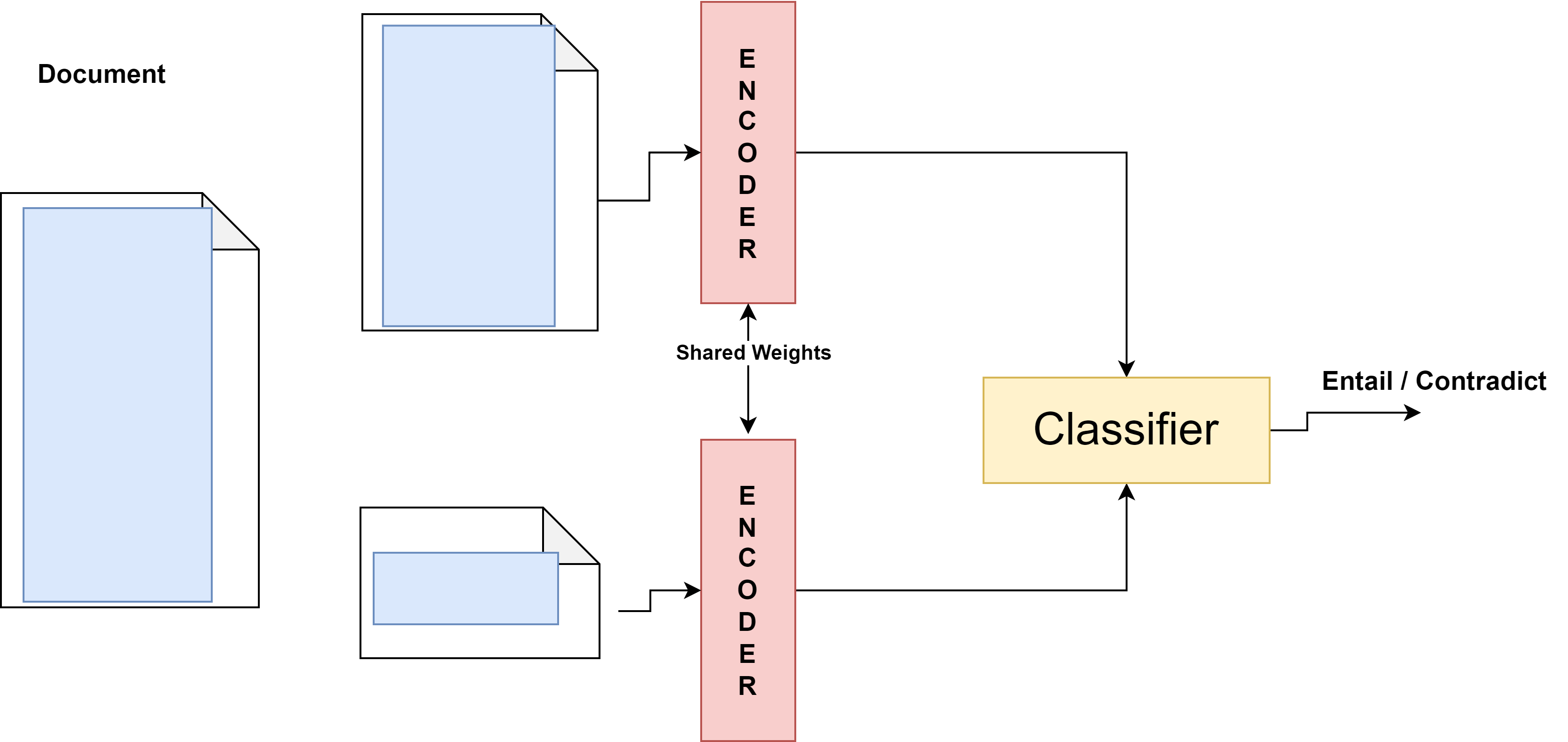
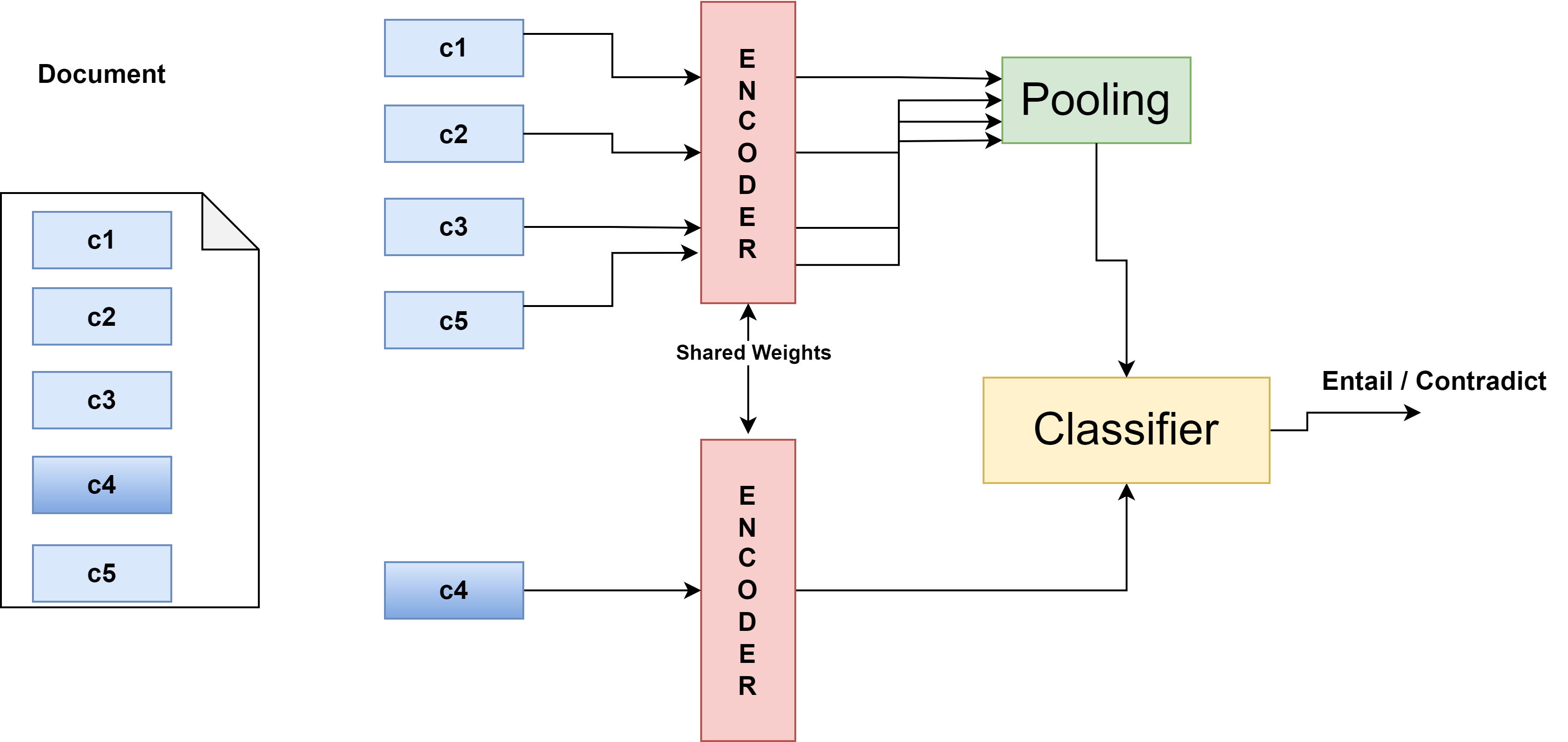
3. Chunk Prediction Encoder (CPE): The paper introduces the CPE, which combines linear-scaling mechanisms with random text span sampling and self-supervised contrastive learning inspired by how experts skim through documents. The CPE works as follows:
- Random Text Span Selection: Random spans are selected from a document to predict whether they belong to the same document.
- Skip Attention Learning: The model uses [CLS] tokens for representing the entire document, and each span’s representation is obtained via average or max pooling.
4. Contrastive Loss: The CPE employs contrastive loss on relevant and irrelevant span pairs to effectively represent documents by aligning related spans with the document context.
5. Experiments and Evaluation:
- Comparison with Baselines: The paper demonstrates that CPE outperforms strong baseline models in generating effective document representations.
- Fine-tuning: The model is fine-tuned on downstream classification tasks, showing superior performance.
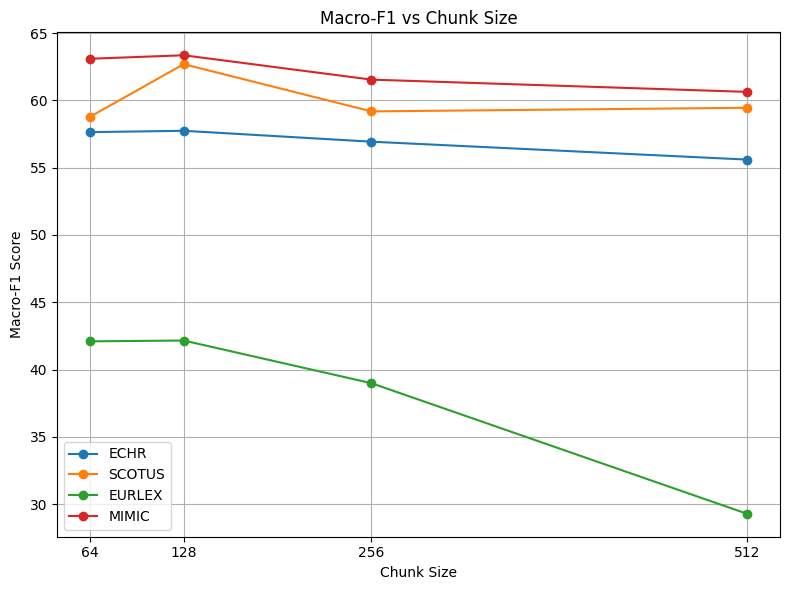
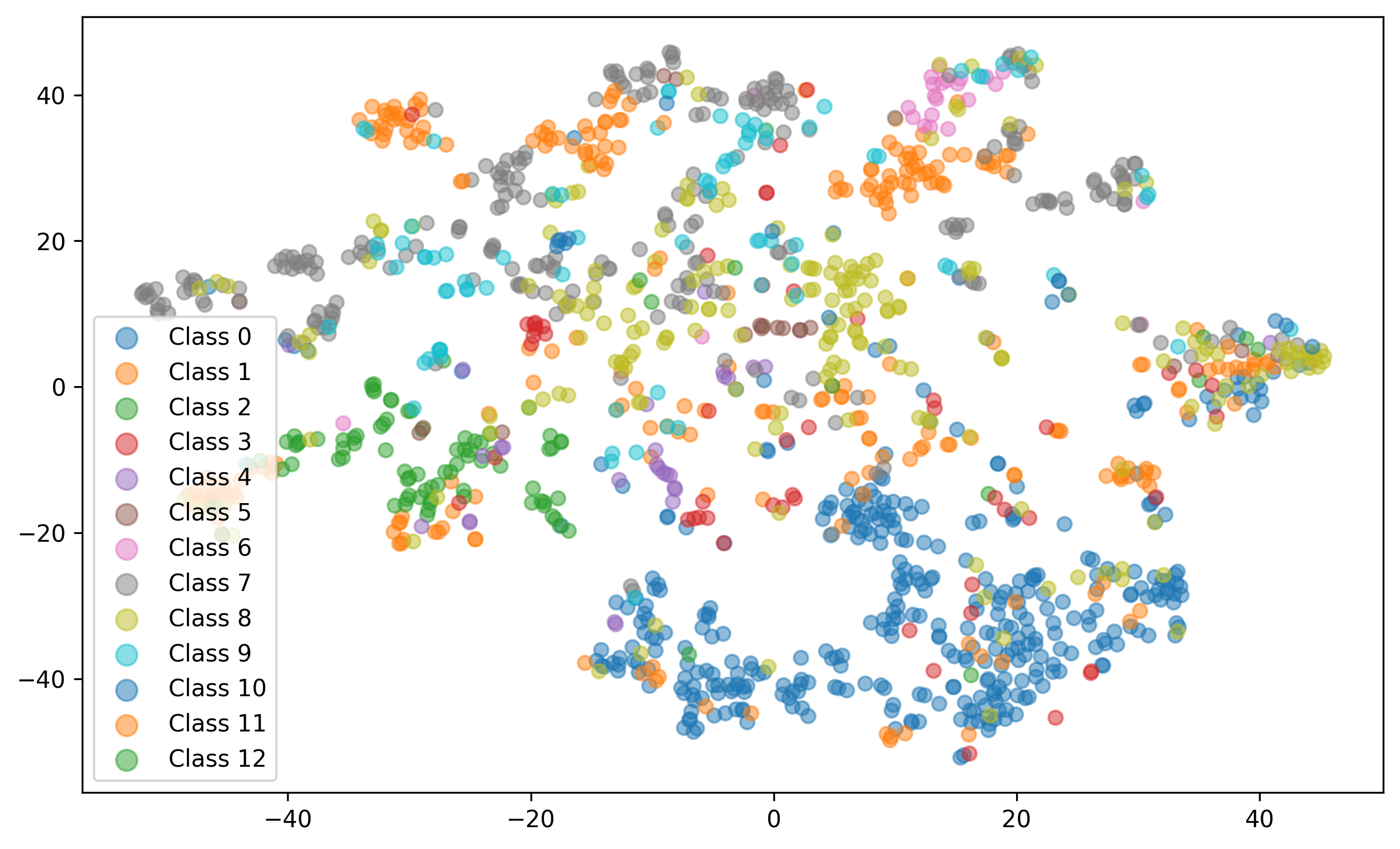
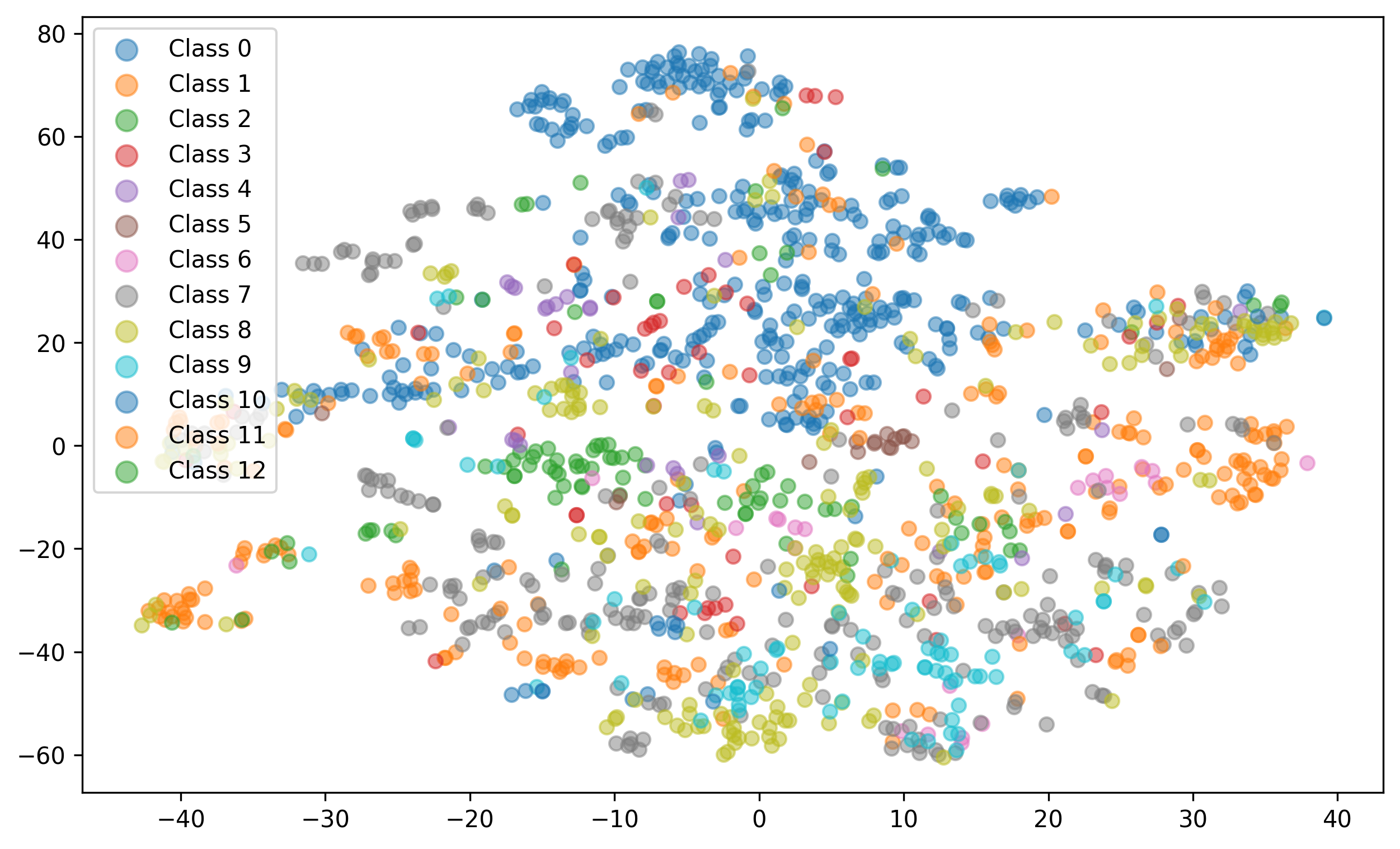
- Ablation Studies: Various span sizes and visualizations are evaluated to analyze the impact of CPE.
6. Long Document Modeling: The paper discusses how hierarchical attention mechanisms are used for long documents, comparing different segmentation methods and self-attention approaches for optimal document classification.
7. Unsupervised Document Representation Learning: Unsupervised learning has been a focus area with models like Word2Vec, Doc2Vec, Skip-Thoughts, and transformer-based models generating contextualized word embeddings. Recent advancements include self-supervised contrastive learning methods that capture consistency across documents.
8. CPE for Efficient Document Representation Learning: The core contribution is the introduction of CPE using pre-trained language models to generate efficient document representations through self-supervised contrastive learning. The process involves:
- Hierarchical Representation Model: Documents are divided into spans, each with a [CLS] token.
- Random Span Selection and NLI Training: Random spans are removed and used to train an NLI classifier to learn dependencies and relevance within documents.
9. Learning Process: The CPE is trained using hierarchical transformer models like Longformer through self-supervised contrastive learning:
- Hierarchical Representation Generation: Vector representations of text spans are generated using pre-trained language models.
- NLI Classifier Training: The model learns document dependencies by predicting if removed spans match other documents’ spans.
- Contrastive Loss: Documents are effectively represented using relevant and irrelevant span pairs.
10. Additional Experiments and Results: The paper validates CPE’s effectiveness through experiments on legal and medical datasets (ECHR, SCOTUS, EURLEX, MIMIC, Biosq), demonstrating superior performance in document classification tasks. Ablation studies analyze the impact of various parameters and span sizes.
Conclusion: This paper presents a novel approach to efficient document representation learning inspired by expert skimming techniques. The proposed CPE model effectively handles long documents through self-supervised contrastive learning, outperforming existing models in various applications, particularly in legal and medical domains.
📄 논문 본문 발췌 (Excerpt)
📸 추가 이미지 갤러리