동적 그래프 지속학습을 위한 CCC 프레임워크
📝 원문 정보
- Title: Condensation-Concatenation Framework for Dynamic Graph Continual Learning
- ArXiv ID: 2512.11317
- 발행일: 2025-12-12
- 저자: Tingxu Yan, Ye Yuan
📝 초록 (Abstract)
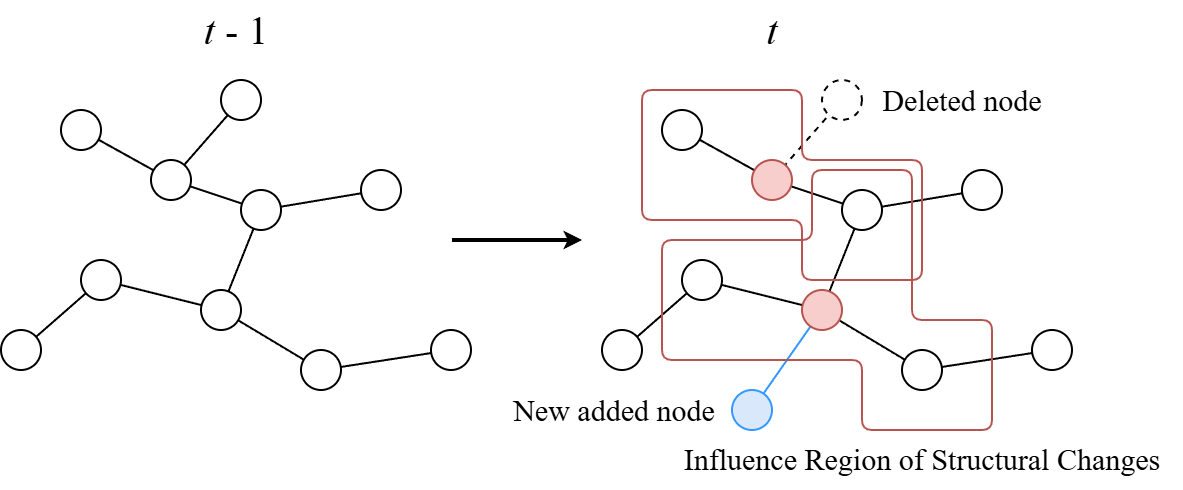
동적인 그래프는 실제 세계의 다양한 상황에서 자주 나타나며, 이러한 구조적 변화는 그래프 신경망(GNNs)에 치명적인 잊음을 초래한다. 지속학습은 동적 그래프로 확장되었지만, 기존 방법들은 기존 노드에 대한 위상 변화의 영향을 간과하고 있다. 이를 해결하기 위해 우리는 새로운 동적 그래프를 위한 지속학습 프레임워크인 CCC(Condensation-Concatenation-based Continual Learning)를 제안한다. 특히, CCC는 과거 그래프 스냅샷을 원래 레이블 분포와 위상 특성을 유지하면서 압축된 의미 표현으로 변환하고, 이를 현재 그래프 표현과 선택적으로 연결한다. 또한, 구조적 업데이트로 인해 기존 노드의 예측 성능 저하를 측정하기 위해 잊음 지표(FM)을 개선하여 동적 그래프 상황에 더 잘 맞도록 보완한다. 광범위한 실험에서 CCC는 네 가지 실제 데이터셋에서 최신 기준 모델보다 우수한 성능을 보여주었다.💡 논문 핵심 해설 (Deep Analysis)
Analysis of the Paper “동적 그래프 지속학습을 위한 압축-연결 프레임워크 CCC”
Abstract:
The paper introduces a new framework called CCC (Condensation-Concatenation Framework for Dynamic Graph Continual Learning), which aims to address the limitations of existing graph neural networks (GNNs) in handling dynamic graphs. It also seeks to improve upon the shortcomings of current continual learning evaluation metrics by considering the temporal characteristics of dynamic graphs.
Background:
Graphs are fundamental structures used in various fields such as social networks for modeling relational data. GNNs have become a standard framework for graph representation learning, effectively extracting node and edge features through deep learning techniques. However, real-world graphs evolve over time with nodes and edges being added or removed, presenting challenges to static GNN models that can lead to catastrophic forgetting—a phenomenon where previously learned knowledge is lost during the process of learning new patterns.
Existing continual learning research has not adequately adapted to dynamic graph settings. Evaluation frameworks often adopt metrics from static domains without considering graph-specific characteristics. Additionally, broad preservation strategies overlook how topological changes affect node representations.
Proposed CCC Framework:
To overcome these limitations, this study proposes the CCC framework, which combines graph condensation and concatenation components to capture temporal changes in dynamic graphs while maintaining representation stability.
Key Components:
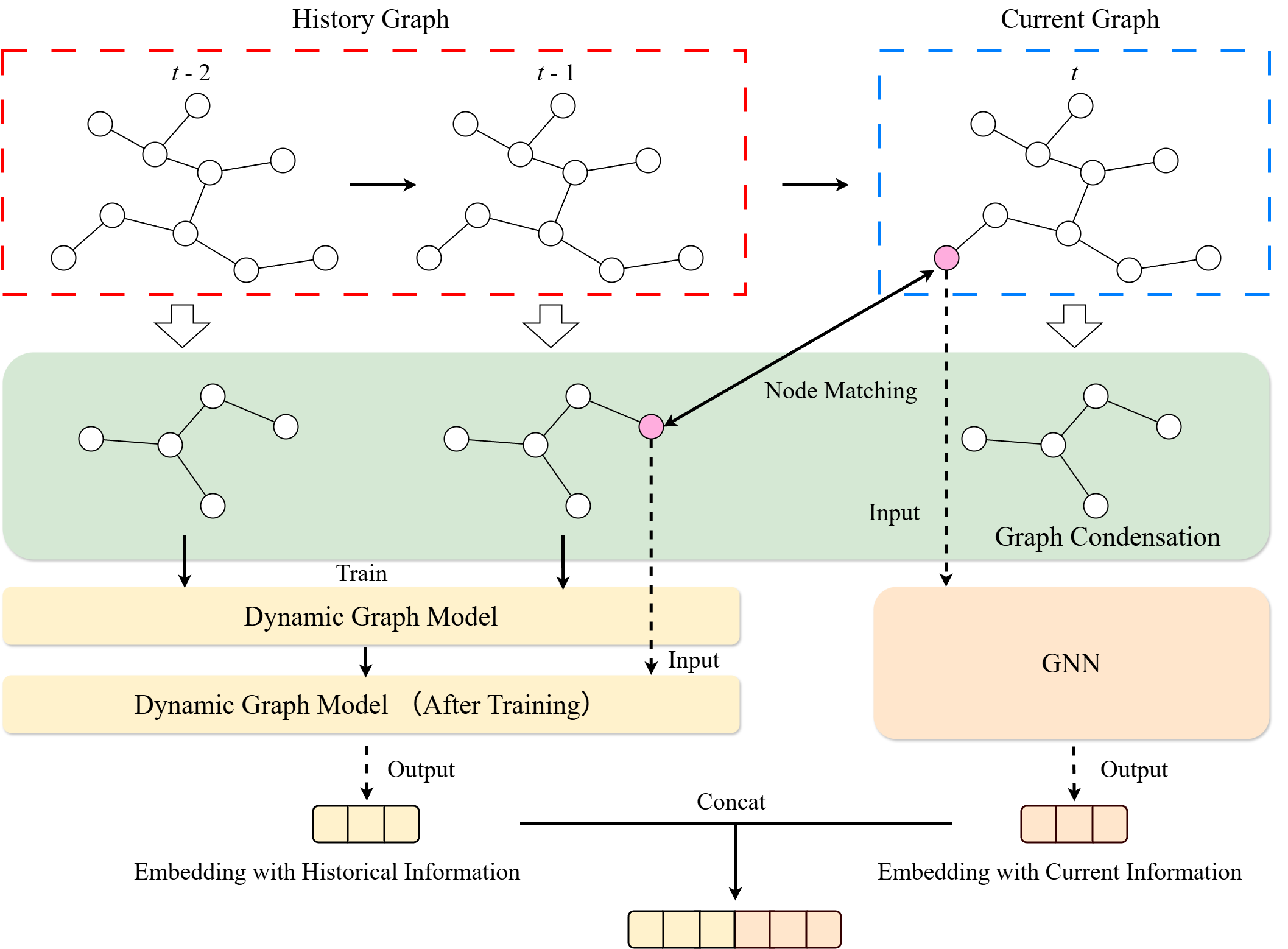
- Graph Condensation: Historical graph snapshots are transformed into condensed semantic representations, saving storage space and increasing efficiency.
- Concatenation: The condensed historical graph representations are combined with the current task’s graph representation to integrate past patterns with new information.
Operation Process:
- Problem Setting: A dynamic graph system is defined as a sequence of graphs that change over time, where each time step t includes a set of nodes V(t) and edges E(t).
- Graph Condensation: Generates condensed graphs based on node label distribution ratios and similarity measurements. The condensed graph retains important information from the original graph while reducing its size.
- Historical Graph Representation Learning: Uses multiple condensed graphs to learn historical graph representations during training, which are then replayed by the model to preserve past patterns.
- Selective Historical Replay: Identifies k-hop subgraphs (influence areas) around nodes where topological changes have occurred and selectively combines condensed graph representations only for affected nodes. This allows efficient learning with minimal information.
Experimental Results:
The CCC framework demonstrated superior performance compared to various continual learning techniques across four real-world dynamic graph datasets: DBLP, Arxiv, Elliptic, and Paper100M. Notably, it recorded low forgetting measure values, effectively demonstrating its capability in preserving knowledge.
Conclusion:
CCC is a robust framework for continual learning on dynamic graphs, enhancing the stability of node representations and efficiently integrating past patterns with new information.
This analysis highlights CCC’s innovative approach to addressing the challenges posed by dynamic graph structures in continual learning scenarios. By combining condensation and concatenation techniques, it offers an effective solution that maintains performance over time while preserving historical knowledge.
📄 논문 본문 발췌 (Excerpt)
📸 추가 이미지 갤러리