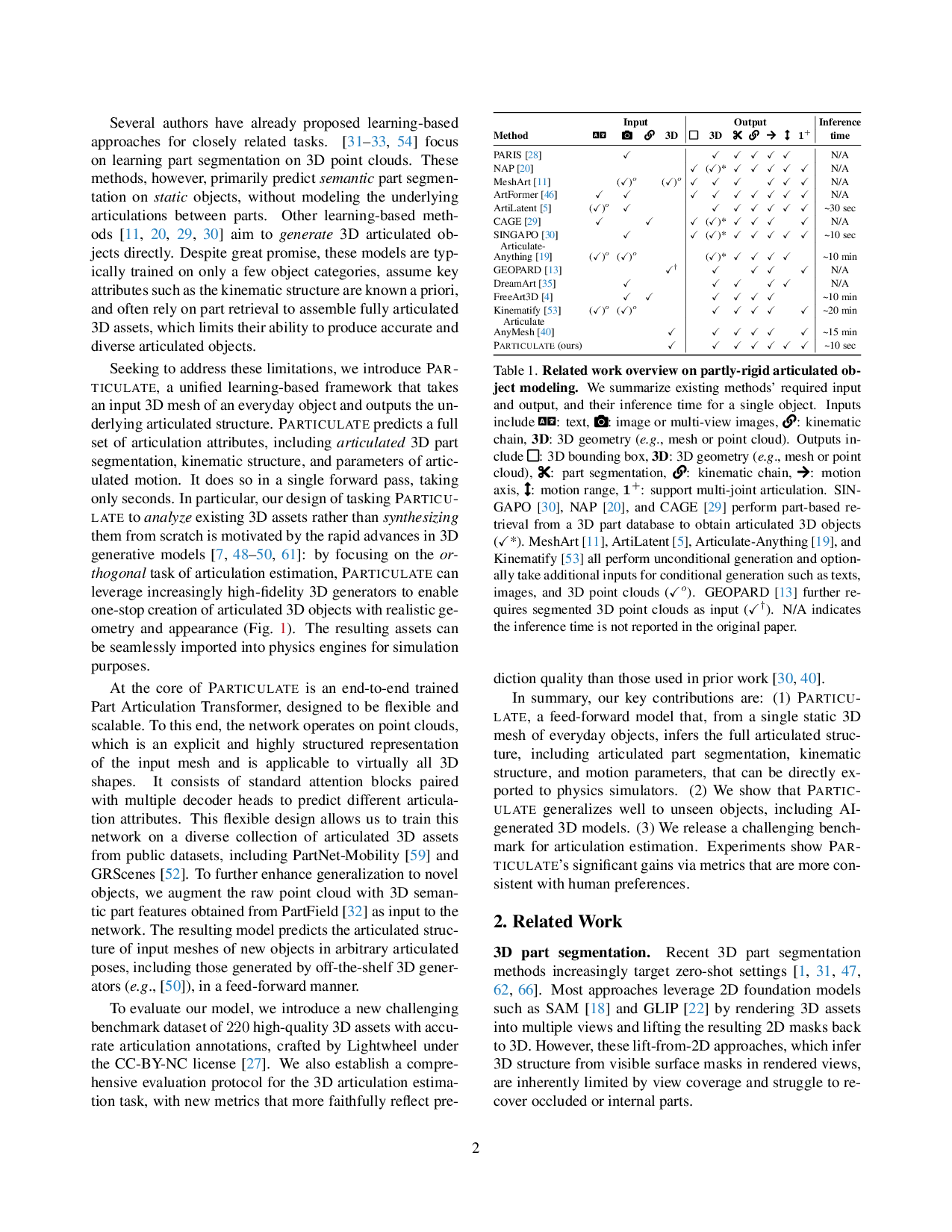
정적 3D 메시에서 빠르게 관절 구조 추출하는 PARTICULATE 모델
📝 원문 정보
- Title: Particulate: Feed-Forward 3D Object Articulation
- ArXiv ID: 2512.11798
- 발행일: 2025-12-12
- 저자: Ruining Li, Yuxin Yao, Chuanxia Zheng, Christian Rupprecht, Joan Lasenby, Shangzhe Wu, Andrea Vedaldi
📝 초록 (Abstract)
도표 1. PARTICULATE로 예측된 접합형 3D 물체. 우리의 모델은 정적인 3D 메시에서 직접 접합 구조를 추론하며, 이는 다양한 물체에 대한 빠른 추론을 가능하게 합니다. 특히 3D 생성 모델로 합성된 물체도 포함됩니다.💡 논문 핵심 해설 (Deep Analysis)

Analysis of the Paper “PARTICULATE: Immediate Joint Structure Extraction from Static 3D Meshes”
Summary:
The paper introduces the PARTICULATE model, which aims to immediately extract joint structures from static 3D meshes based on the observed movements and interactions among multiple parts in everyday objects. Traditional approaches have modeled various daily joint objects through procedural generation but face challenges when scaling up to large sets of real-world objects. The authors adopt a learning-based approach to address these issues.
Differences from Previous Research:
- Learning-Based Approach: Unlike previous methods that relied on rule-based or manually crafted models for predicting joint structures, PARTICULATE leverages pre-existing knowledge of joint structures learned from diverse 3D assets, enhancing its generalization capabilities.
- Single Forward-Pass Inference: The model performs a single forward-pass inference to predict joint segmentation, kinematic structure, and motion parameters from the input 3D mesh. This makes it significantly faster than existing methods.
- Compatibility with AI-Generated Models: PARTICULATE can be applied to objects generated by off-the-shelf 3D generative models.
Key Contributions:
- PARTICULATE Model: A feedforward model that extracts entire joint structures from static 3D meshes, outputting joint part segmentation, kinematic structure, and motion parameters.
- Generalization Capability: The model demonstrates good generalization performance across various categories of AI-generated 3D models.
- Benchmark Dataset: Introduces a new challenging benchmark dataset for joint extraction to evaluate the quality of objects and accuracy of joint structures.
How PARTICULATE Works:
- Input: Receives a static 3D mesh (e.g., furniture, tools) as input.
- Point Cloud Conversion: Converts the 3D mesh into a point cloud representation, which is applicable to all 3D shapes and compatible with most data structures.
- Network Architecture: Uses Part Articulation Transformer (PAT), based on standard transformer architecture, taking the point cloud and part queries as inputs to predict joint structure.
- Joint Structure Extraction:
- Joint Segmentation: Predicts masks for each point to segment the 3D mesh into multiple joint parts.
- Kinematic Tree: Predicts a soft kinematic tree representing hierarchical relationships between parts.
- Motion Parameters: Predicts motion type, range, and direction for each part.
- Final Output: The inferred joint structure is exported in URDF format for use in physics simulators.
Conclusion:
PARTICULATE is a powerful learning-based model that can accurately and immediately extract joint structures from static 3D meshes. This model has potential applications in various fields, including robotic manipulation, digital twin creation, and physical simulation.
This analysis provides an overview of the PARTICULATE model’s innovative approach to extracting joint structures from static 3D meshes, highlighting its advantages over traditional methods and its broad applicability across different domains.
📄 논문 본문 발췌 (Excerpt)
📸 추가 이미지 갤러리