연속 행동 공간에서 가우시안 프로세스 회귀를 활용한 루트 병렬 MCTS 통계 통합
📝 원문 정보
- Title: Gaussian Process Aggregation for Root-Parallel Monte Carlo Tree Search with Continuous Actions
- ArXiv ID: 2512.09727
- 발행일: 2025-12-10
- 저자: Junlin Xiao, Victor-Alexandru Darvariu, Bruno Lacerda, Nick Hawes
📝 초록 (Abstract)
Monte Carlo Tree Search(MCTS)는 온라인 계획의 핵심 알고리즘으로, 시간 제약이 있지만 최상의 성능을 원하는 상황에서 루트 병렬 변형이 널리 사용됩니다. 연속적인 행동 공간 환경에서는 여러 스레드로부터 얻은 통계를 어떻게 가장 잘 통합할지에 대한 질문은 중요한 문제지만, 아직 충분히 탐구되지 않았습니다. 본 연구에서는 가우시안 프로세스 회귀를 활용하여 환경에서 시도되지 않은 유망한 행동의 가치 추정치를 얻는 방법을 제안합니다. 우리는 6개의 다른 도메인에 걸쳐 체계적인 평가를 수행하고, 우리의 접근법이 기존의 통합 전략보다 우수하며, 추론 시간은 소폭 증가하는 것을 보여줍니다.💡 논문 핵심 해설 (Deep Analysis)
Analysis of the Paper “Utilizing Gaussian Process Regression for Statistical Integration in Root Parallel MCTS in Continuous Action Spaces”
Introduction:
The paper introduces a novel method called GPR2P (Gaussian Process Regression for Root Parallel Monte Carlo Tree Search) to enhance statistical integration within root parallel Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS). The authors highlight that while MCTS is widely used due to its anytime applicability and effectiveness in planning under time or simulation budget constraints, its performance heavily relies on the quality of simulation results. This reliance can lead to difficulties in identifying strong actions when resources are limited.
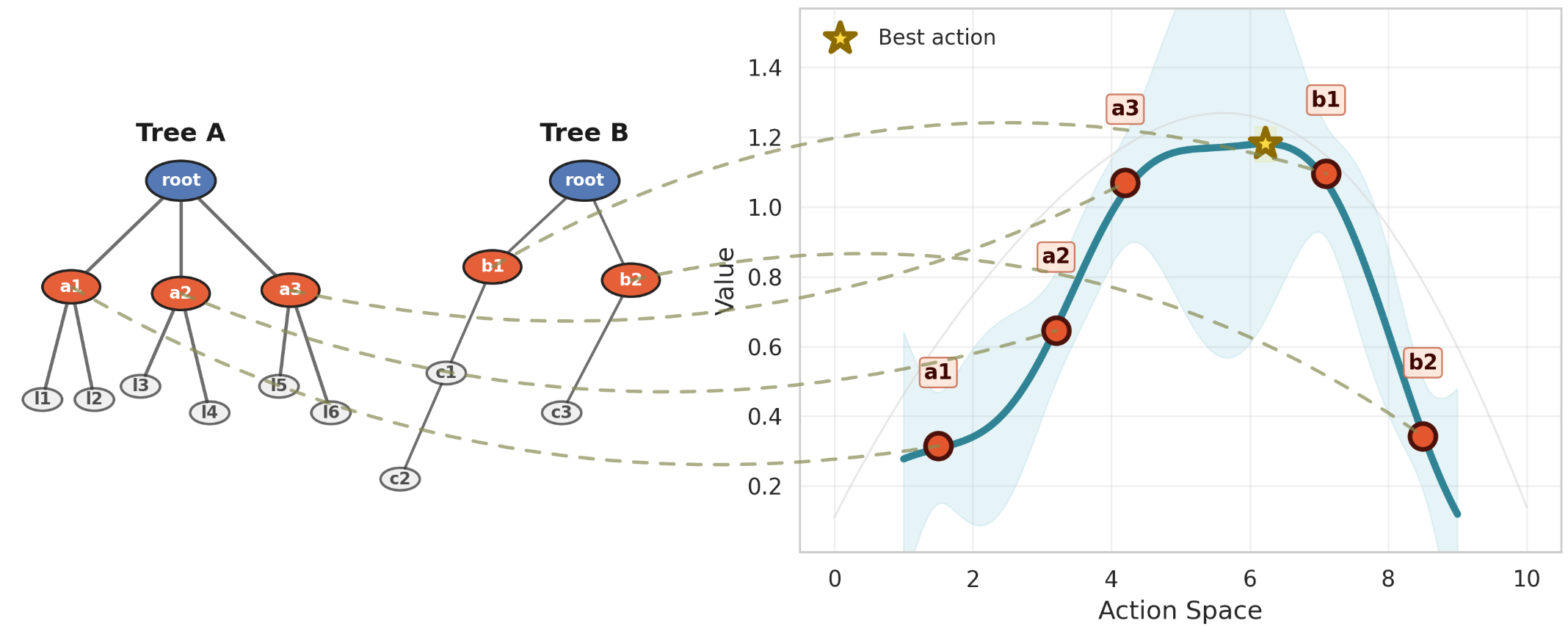
Root Parallel MCTS improves upon traditional MCTS by running multiple independent MCTS instances and integrating their outcomes to select a final action. However, an optimal method for aggregating these results remains a significant challenge, especially in continuous action spaces where each sampled action is unique, making conventional majority voting approaches ineffective.
Existing Methods vs. GPR2P:
The authors compare existing methods used for statistical integration within root parallel MCTS with their proposed GPR2P approach:
- Max Algorithm: Selects the state-action pair with the highest estimated value.
- Most Visited Algorithm: Chooses the action that has been visited most frequently.
Kurzer, Hörtnagl, and Zöllner (2020) introduced two methods for integrating all trees using action similarity: Similarity Vote and Similarity Merge. These methods use an Euclidean distance-based similarity matrix to establish connections between actions.
GPR2P differs from these existing approaches by constructing a statistical model over the entire action space, thereby expanding the selection range beyond just sampled actions. It applies a visitation threshold τ to filter out sufficiently explored actions and performs Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) on these filtered actions.
Experiments and Results:
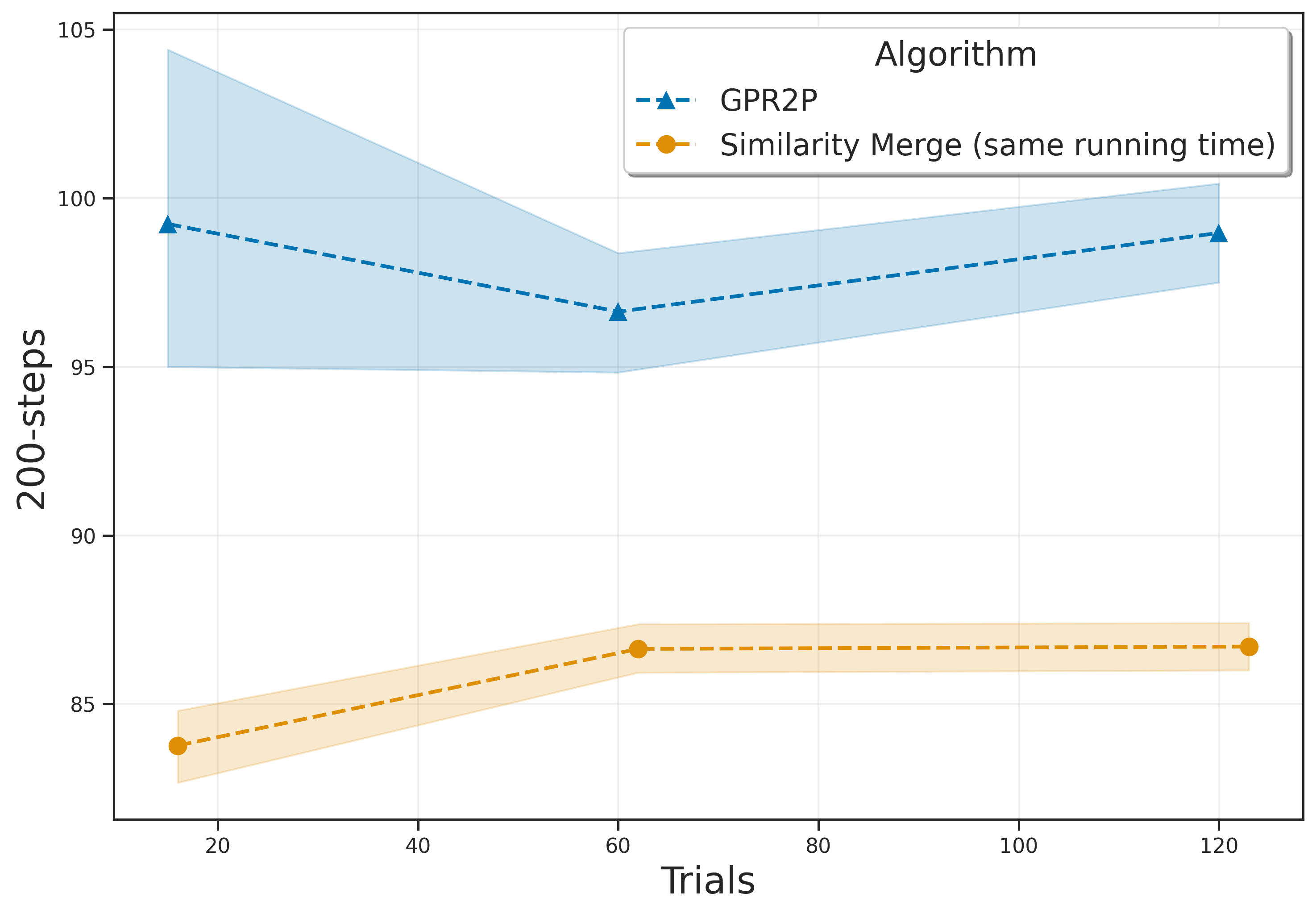
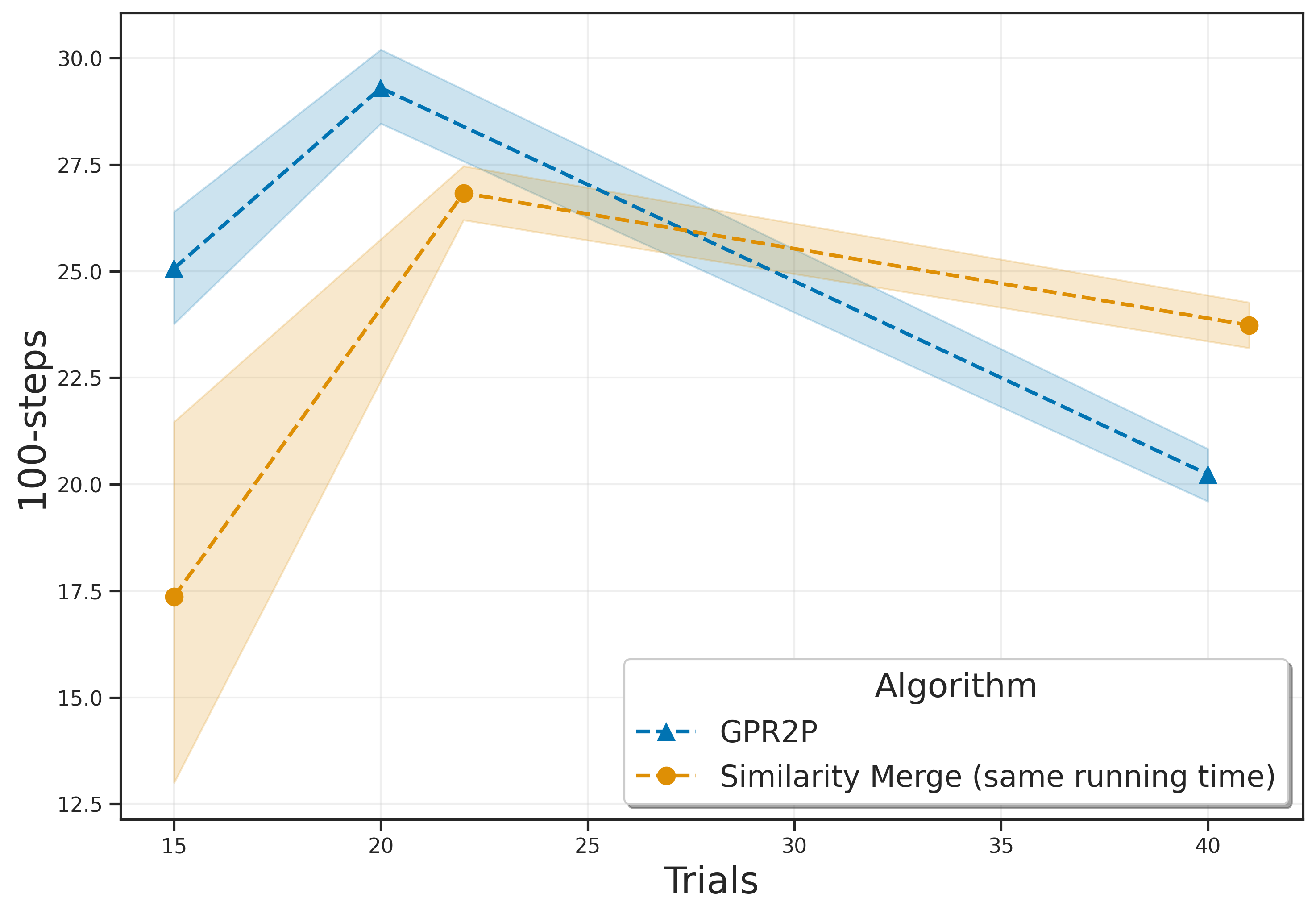
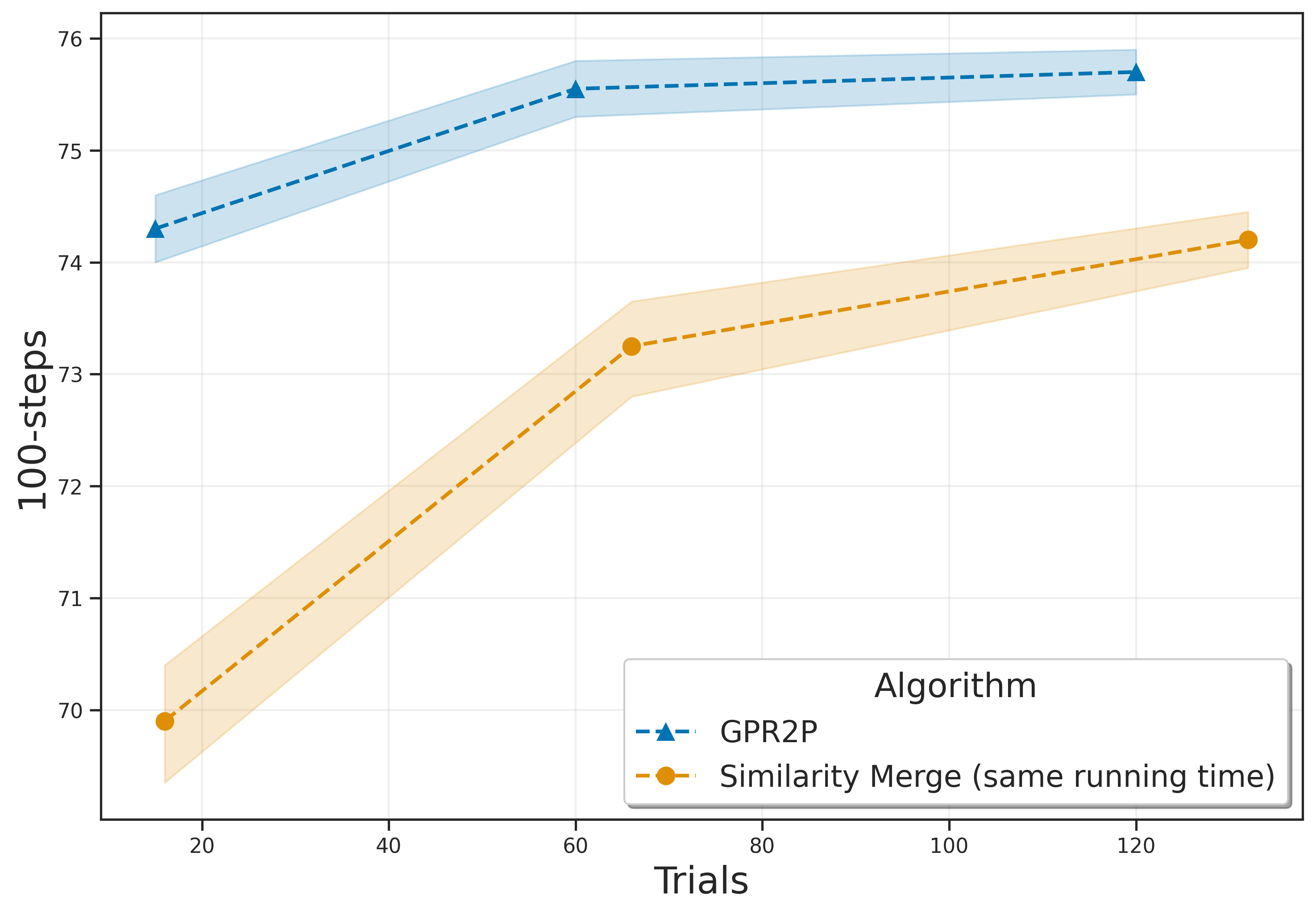
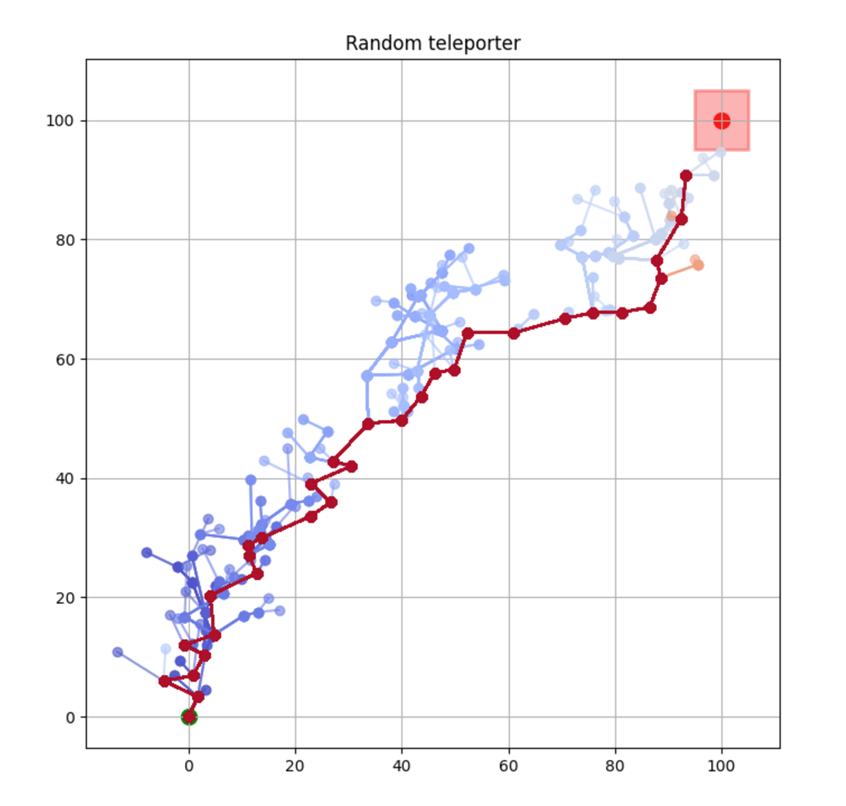
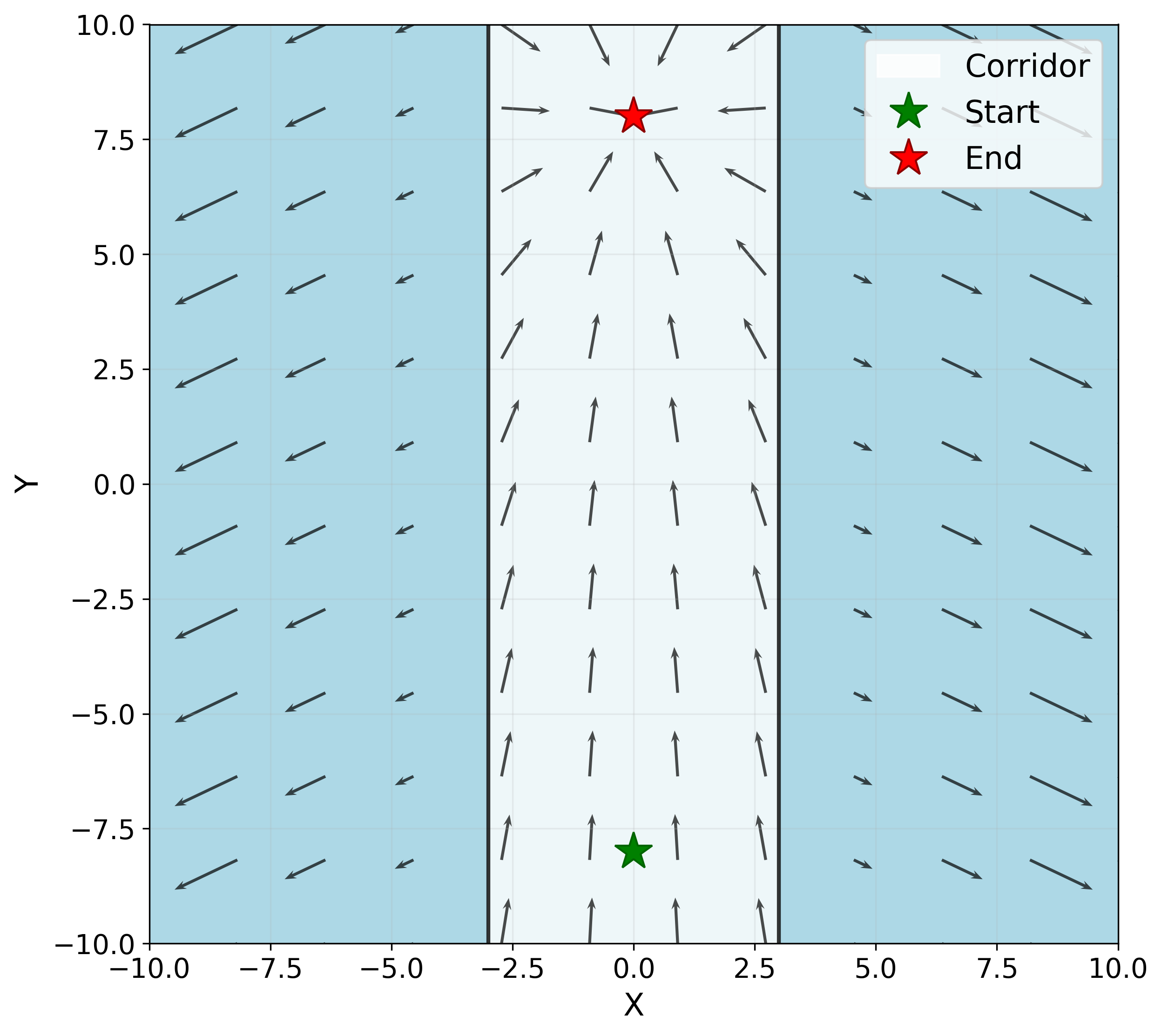
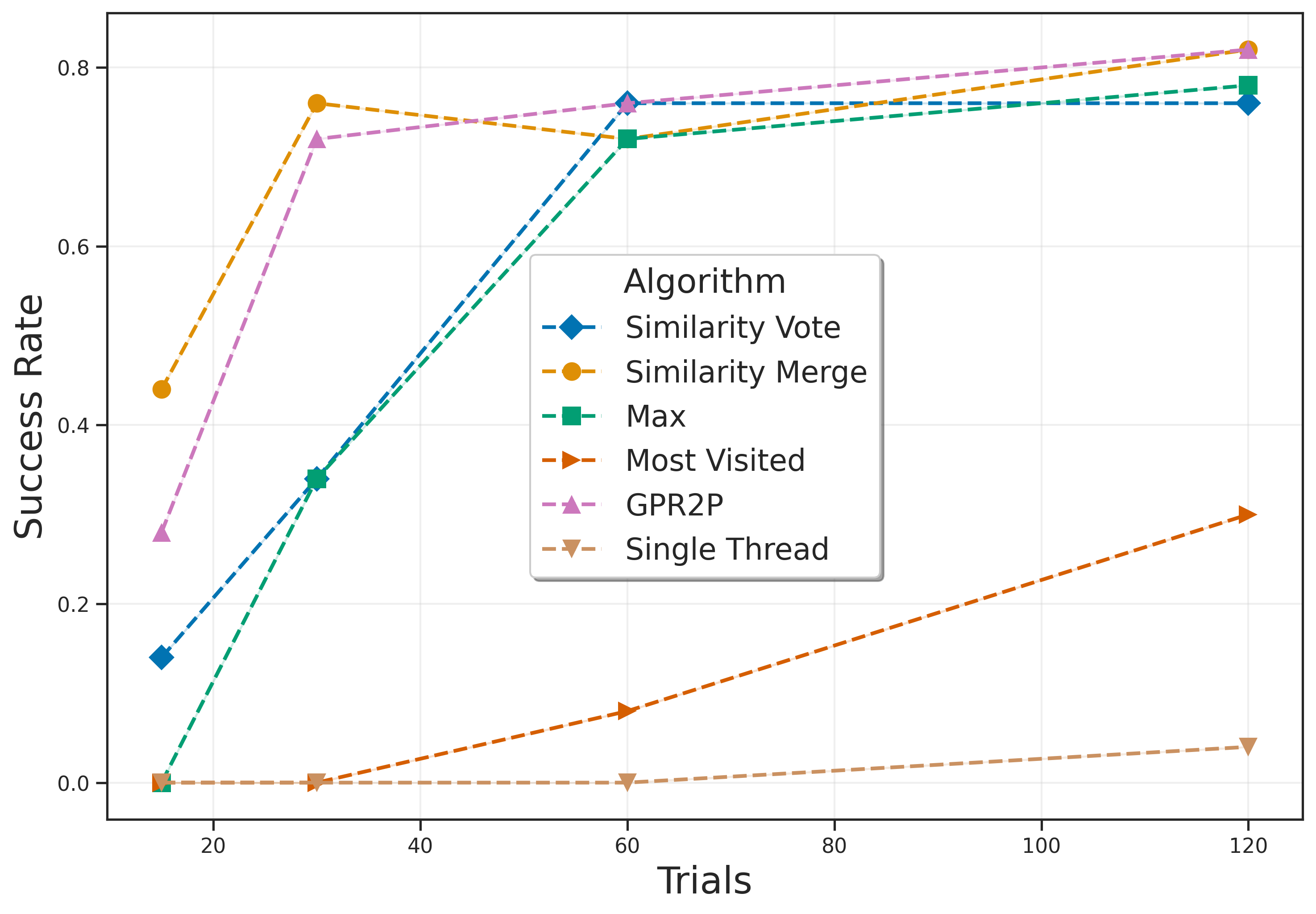
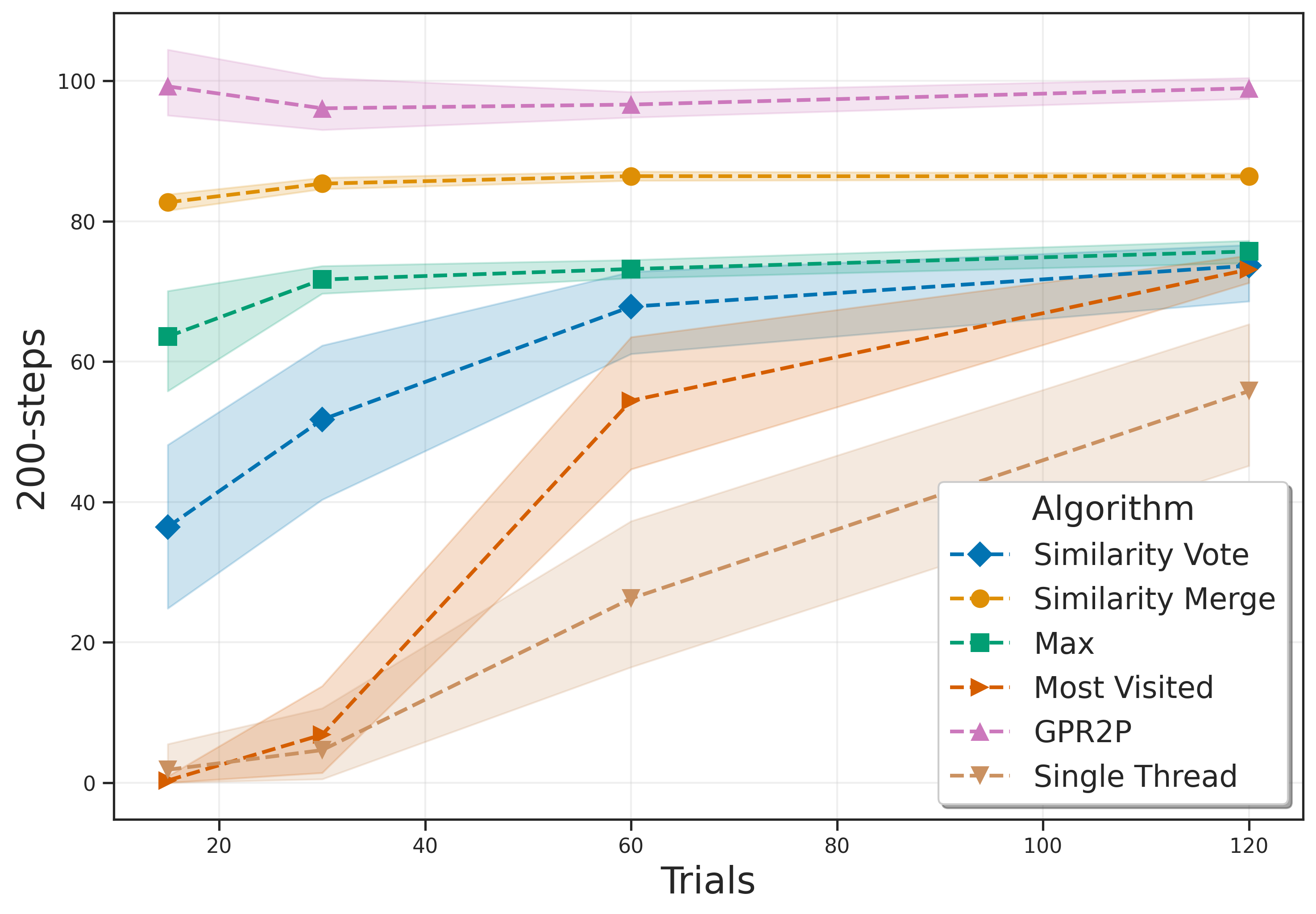
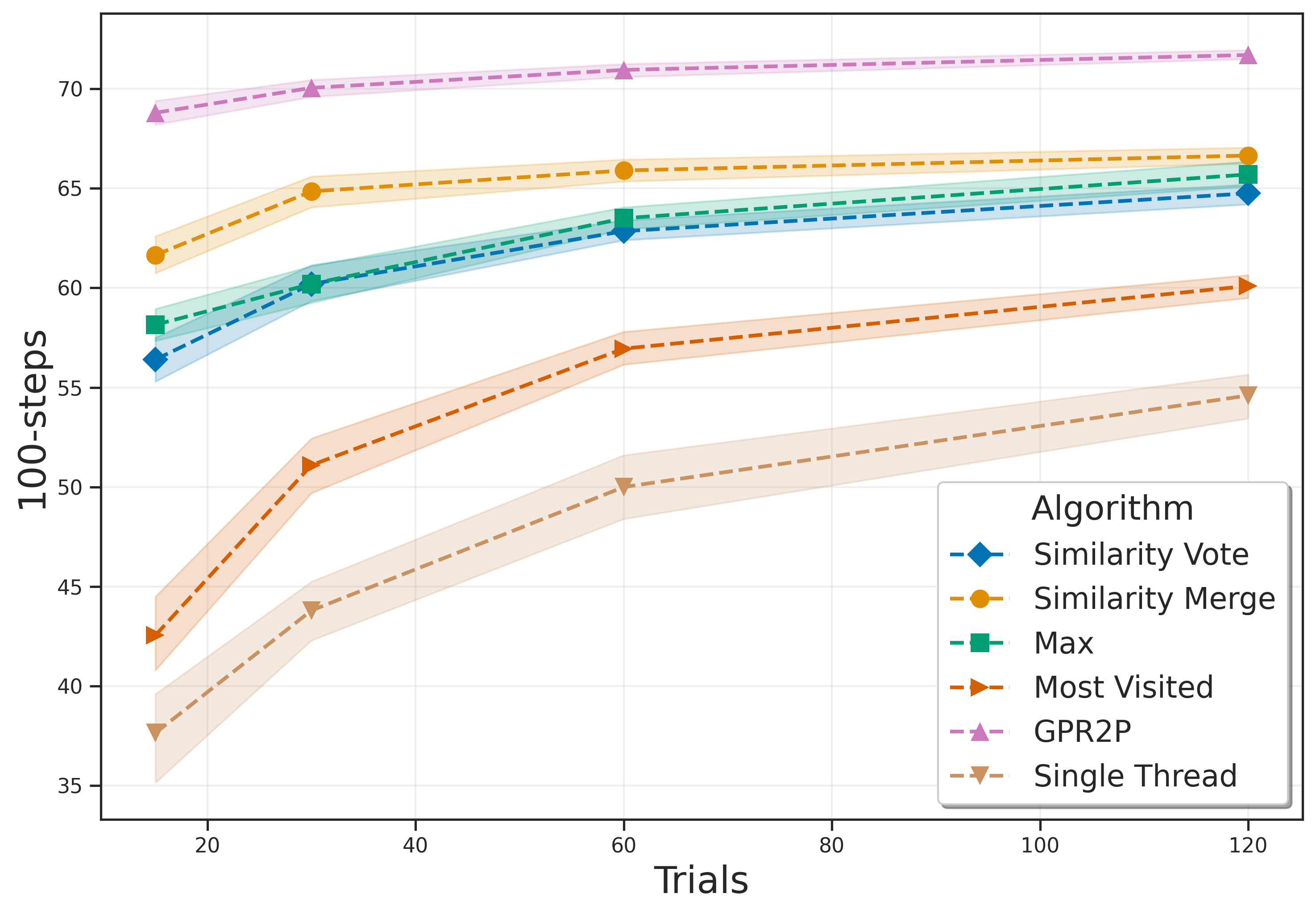
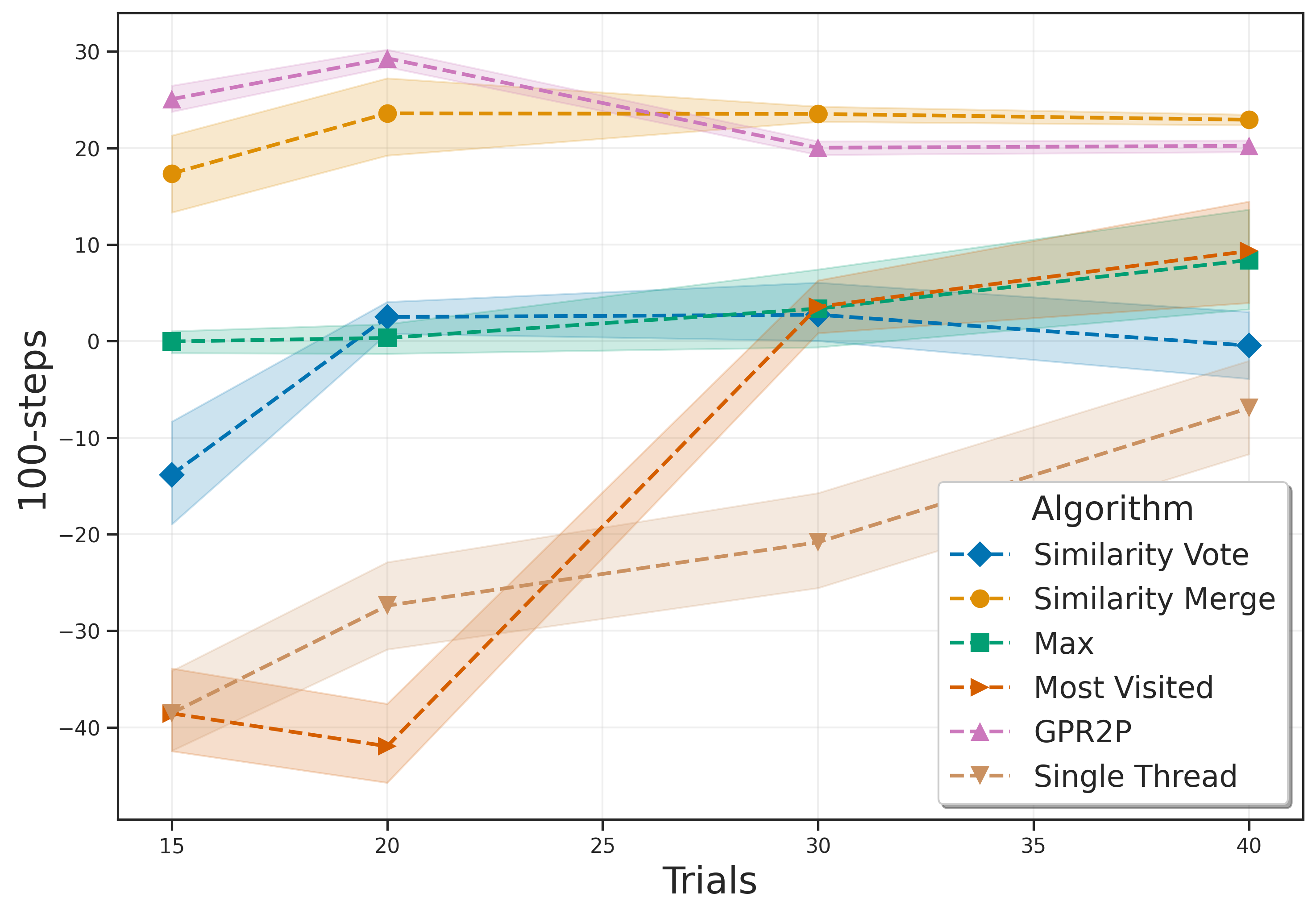
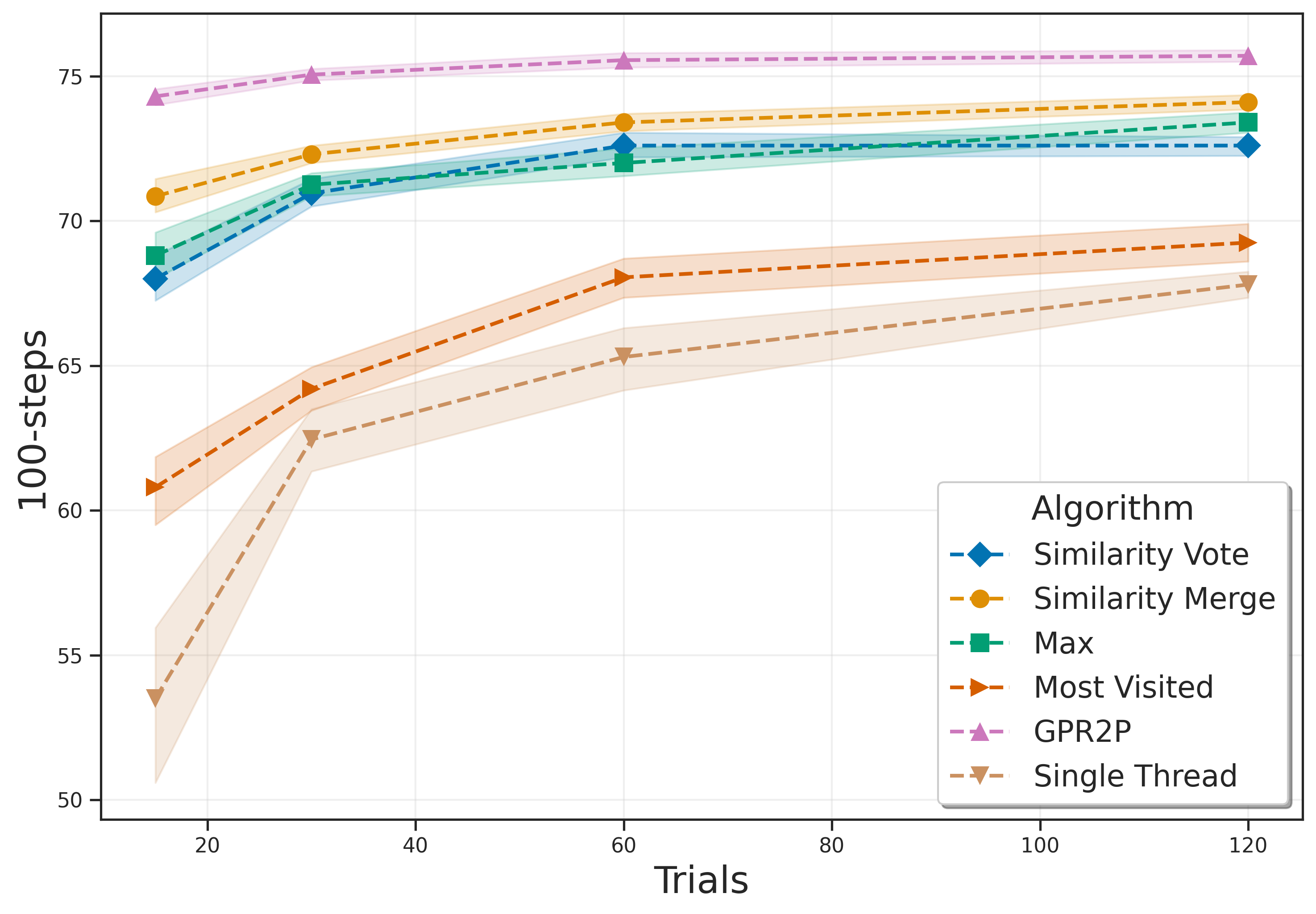
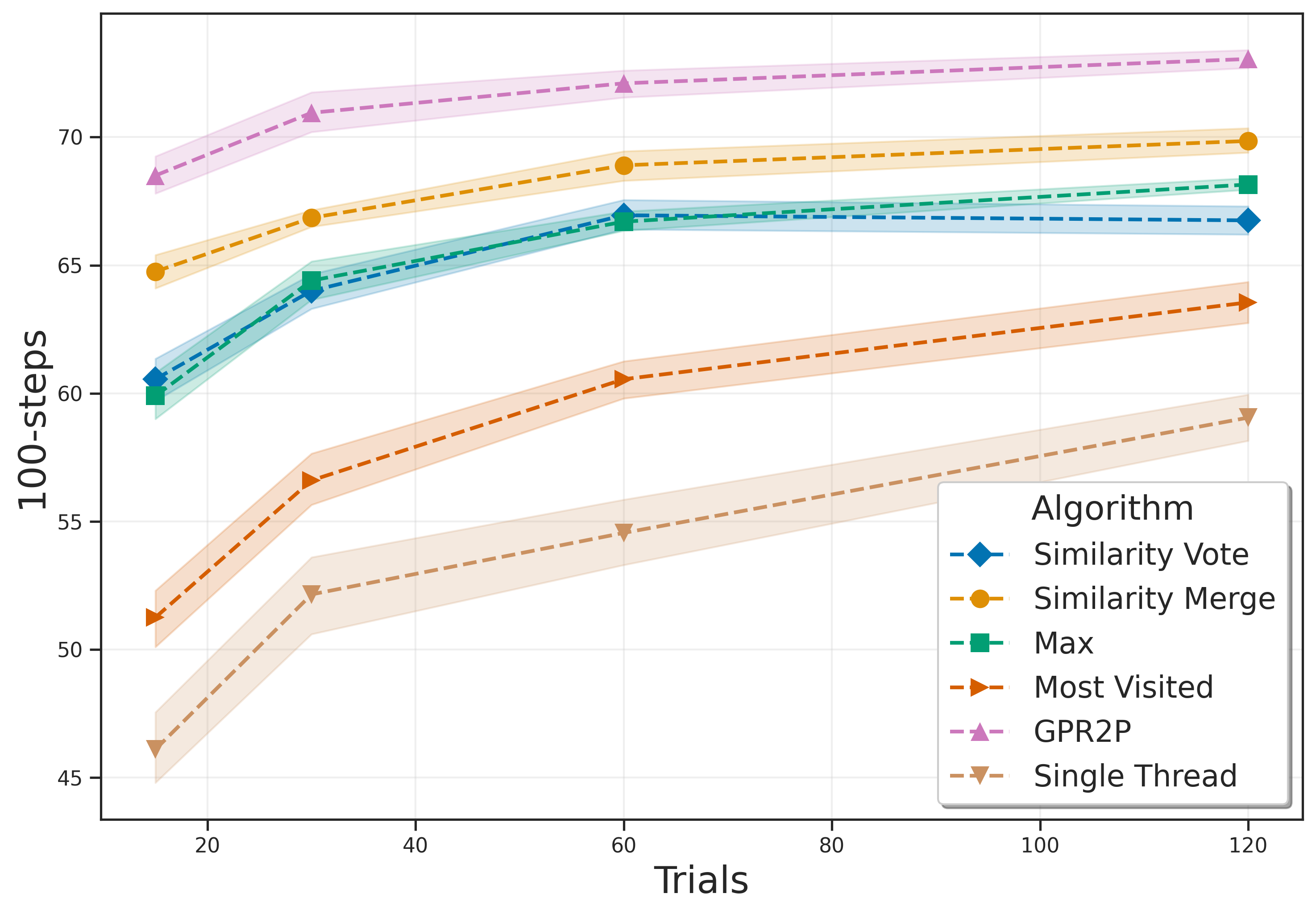
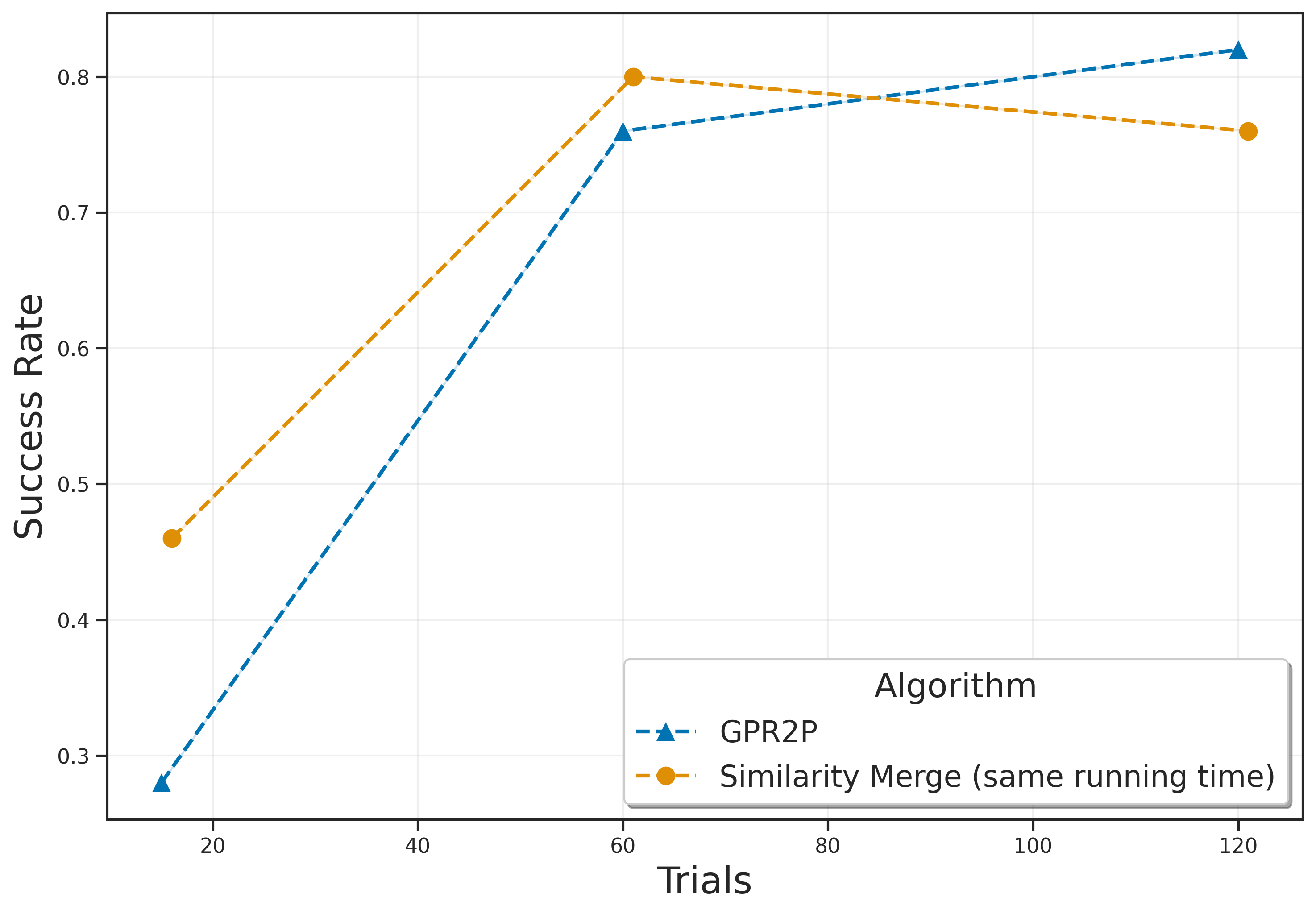
The authors conducted experiments in six different environments: Lunar Lander, Mountain Car, Pendulum, Random Teleporter, Wide Corridor, and Narrow Corridor. The results indicate that GPR2P consistently outperforms both existing methods and single-threaded MCTS across all environments. Notably, GPR2P showed better performance compared to Similarity Merge, with the performance gap decreasing as the number of simulations increased.
Conclusion:
The paper proposes a new method called GPR2P for improving statistical integration in root parallel MCTS by utilizing Gaussian Process Regression. Experimental results demonstrate that GPR2P outperforms existing methods across various environments. Future research directions include further enhancing the efficiency of GPR2P and exploring its application in diverse fields.
Summary:
The paper presents a significant advancement in the field of Monte Carlo Tree Search, particularly for continuous action spaces. By leveraging Gaussian Process Regression, GPR2P offers a more robust method for integrating results from multiple MCTS instances, leading to improved performance across different environments. This research not only enhances the capabilities of root parallel MCTS but also opens up new avenues for its application in complex decision-making scenarios.
📄 논문 본문 발췌 (Excerpt)
📸 추가 이미지 갤러리